Building the mammalian testis: origins, differentiation, and assembly of the component cell populations
- PMID: 24240231
- PMCID: PMC3841730
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.228080.113
Building the mammalian testis: origins, differentiation, and assembly of the component cell populations
Abstract
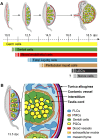
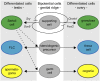
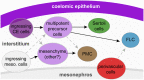
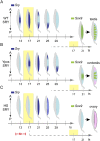
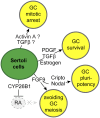
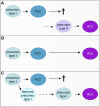
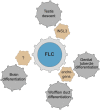
Development of testes in the mammalian embryo requires the formation and assembly of several cell types that allow these organs to achieve their roles in male reproduction and endocrine regulation. Testis development is unusual in that several cell types such as Sertoli, Leydig, and spermatogonial cells arise from bipotential precursors present in the precursor tissue, the genital ridge. These cell types do not differentiate independently but depend on signals from Sertoli cells that differentiate under the influence of transcription factors SRY and SOX9. While these steps are becoming better understood, the origins and roles of many testicular cell types and structures-including peritubular myoid cells, the tunica albuginea, the arterial and venous blood vasculature, lymphatic vessels, macrophages, and nerve cells-have remained unclear. This review synthesizes current knowledge of how the architecture of the testis unfolds and highlights the questions that remain to be explored, thus providing a roadmap for future studies that may help illuminate the causes of XY disorders of sex development, infertility, and testicular cancers.
Keywords: Leydig cells; Sertoli cells; disorder of sex development; fertility; organogenesis; sex determination.
Figures


References
-
- Albrecht KH, Eicher EM 2001. Evidence that Sry is expressed in pre-Sertoli cells and Sertoli and granulosa cells have a common precursor. Dev Biol 240: 92–107 - PubMed
-
- Allen LG, Wilson FJ, Macdonald GJ 1989. Neuropeptide Y-containing nerves in the rat gonads: Sex difference and development. Biol Reprod 40: 371–378 - PubMed
-
- Anderson R, Copeland TK, Schöler H, Heasman J, Wylie C 2000. The onset of germ cell migration in the mouse embryo. Mech Dev 91: 61–68 - PubMed
-
- Anesetti G, Lombide P, D'Albora H, Ojeda SR 2001. Intrinsic neurons in the human ovary. Cell Tissue Res 306: 231–237 - PubMed
-
- Azhar S, Leers-Sucheta S, Reaven E 2003. Cholesterol uptake in adrenal and gonadal tissues: The SR-BI and ‘selective’ pathway connection. Front Biosci 8: s998–s1029 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
