Promoting remyelination in multiple sclerosis-recent advances
- PMID: 24242317
- PMCID: PMC3853368
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-013-0146-8
Promoting remyelination in multiple sclerosis-recent advances
Erratum in
- Drugs. 2014 Jan;74(1):157. Jolanda Münzel, E [corrected to Münzel, E Jolanda]
Abstract
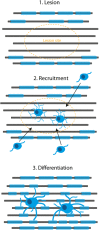
We review the current state of knowledge of remyelination in multiple sclerosis (MS), concentrating on advances in the understanding of the pathology and the regenerative response, and we summarise progress on the development of new therapies to enhance remyelination aimed at reducing progressive accumulation of disability in MS. We discuss key target pathways identified in experimental models, as although most identified targets have not yet progressed to the stage of being tested in human clinical trials, they may provide treatment strategies for demyelinating diseases in the future. Finally, we discuss some of the problems associated with testing this class of drugs, where they might fit into the therapeutic arsenal and the gaps in our knowledge.
Figures

References
-
- Pugliatti M, Sotgiu S, Rosati G. The worldwide prevalence of multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2002;104(3):182–191. - PubMed
-
- Costenbader KH, Gay S, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, et al. Genes, epigenetic regulation and environmental factors: which is the most relevant in developing autoimmune diseases? Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11(8):604–609. - PubMed
-
- Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, et al. A quantitative analysis of oligodendrocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions. A study of 113 cases. Brain. 1999;122(Pt 12):2279–2295. - PubMed
-
- Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, et al. Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(13):938–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

