Effects of exercise intensity on postprandial improvement in glucose disposal and insulin sensitivity in prediabetic adults
- PMID: 24243632
- PMCID: PMC3879669
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2013-2687
Effects of exercise intensity on postprandial improvement in glucose disposal and insulin sensitivity in prediabetic adults
Abstract
Background: A single bout of exercise improves postprandial glycemia and insulin sensitivity in prediabetic patients; however, the impact of exercise intensity is not well understood. The present study compared the effects of acute isocaloric moderate (MIE) and high-intensity (HIE) exercise on glucose disposal and insulin sensitivity in prediabetic adults.
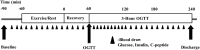
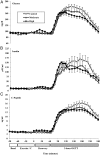
Methods: Subjects (n=18; age 49±14 y; fasting glucose 105±11 mg/dL; 2 h glucose 170±32 mg/dL) completed a peak O2 consumption/lactate threshold (LT) protocol plus three randomly assigned conditions: 1) control, 1 hour of seated rest, 2) MIE (at LT), and 3) HIE (75% of difference between LT and peak O2 consumption). One hour after exercise, subjects received an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). Plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide concentrations were sampled at 5- to 10-minute intervals at baseline, during exercise, after exercise, and for 3 hours after glucose ingestion. Total, early-phase, and late-phase area under the glucose and insulin response curves were compared between conditions. Indices of insulin sensitivity (SI) were derived from OGTT data using the oral minimal model.
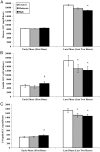
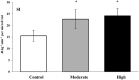
Results: Compared with control, SI improved by 51% (P=.02) and 85% (P<.001) on the MIE and HIE days, respectively. No differences in SI were observed between the exercise conditions (P=.62). Improvements in SI corresponded to significant reductions in the glucose, insulin, and C-peptide area under the curve values during the late phase of the OGTT after HIE (P<.05), with only a trend for reductions after MIE.
Conclusion: These results suggest that in prediabetic adults, acute exercise has an immediate and intensity-dependent effect on improving postprandial glycemia and insulin sensitivity.
Figures
References
-
- Cavalot F, Petrelli A, Traversa M, et al. Postprandial blood glucose is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular events than fasting blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus, particularly in women: lessons from the San Luigi Gonzaga Diabetes Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:813–819 - PubMed
-
- Woerle HJ, Neumann C, Zschau S, et al. Impact of fasting and postprandial glycemia on overall glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: importance of postprandial glycemia to achieve target HbA1c levels. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77:280–285 - PubMed
-
- Colberg SR, Albright AL, Blissmer BJ, et al. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association: joint position statement. Exercise and type 2 diabetes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42:2282–2303 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

