A prominent lack of IgG1-Fc fucosylation of platelet alloantibodies in pregnancy
- PMID: 24243971
- PMCID: PMC3901064
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-09-527978
A prominent lack of IgG1-Fc fucosylation of platelet alloantibodies in pregnancy
Abstract
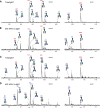
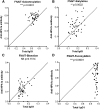
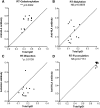
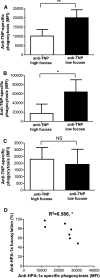
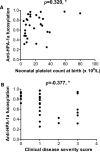
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) formed during pregnancy against human platelet antigens (HPAs) of the fetus mediates fetal or neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (FNAIT). Because antibody titer or isotype does not strictly correlate with disease severity, we investigated by mass spectrometry variations in the glycosylation at Asn297 in the IgG Fc because the composition of this glycan can be highly variable, affecting binding to phagocyte IgG-Fc receptors (FcγR). We found markedly decreased levels of core fucosylation of anti-HPA-1a-specific IgG1 from FNAIT patients (n = 48), but not in total serum IgG1. Antibodies with a low amount of fucose displayed higher binding affinity to FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIIb, but not to FcγRIIa, compared with antibodies with a high amount of Fc fucose. Consequently, these antibodies with a low amount of Fc fucose showed enhanced phagocytosis of platelets using FcγRIIIb(+) polymorphonuclear cells or FcγRIIIa(+) monocytes as effector cells, but not with FcγRIIIa(-) monocytes. In addition, the degree of anti-HPA-1a fucosylation correlated positively with the neonatal platelet counts in FNAIT, and negatively to the clinical disease severity. In contrast to the FNAIT patients, no changes in core fucosylation were observed for anti-HLA antibodies in refractory thrombocytopenia (post platelet transfusion), indicating that the level of fucosylation may be antigen dependent and/or related to the immune milieu defined by pregnancy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Core fucosylation and IgG function in NAIT.Blood. 2014 Jan 23;123(4):463-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-12-539965. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24458274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semple JW, Italiano JE, Jr, Freedman J. Platelets and the immune continuum. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(4):264–274. - PubMed
-
- Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Anti-inflammatory actions of intravenous immunoglobulin. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:513–533. - PubMed
-
- Shields RL, Lai J, Keck R, et al. Lack of fucose on human IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human Fcgamma RIII and antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(30):26733–26740. - PubMed
-
- Sondermann P, Huber R, Oosthuizen V, Jacob U. The 3.2-A crystal structure of the human IgG1 Fc fragment-Fc gammaRIII complex. Nature. 2000;406(6793):267–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

