Essential functions for ID proteins at multiple checkpoints in invariant NKT cell development
- PMID: 24244015
- PMCID: PMC3864619
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301521
Essential functions for ID proteins at multiple checkpoints in invariant NKT cell development
Abstract
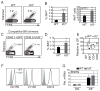
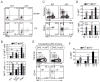
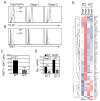
Invariant NKT (iNKT) cells display characteristics of both adaptive and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs). Like other ILCs, iNKT cells constitutively express ID proteins, which antagonize the E protein transcription factors that are essential for adaptive lymphocyte development. However, unlike ILCs, ID2 is not essential for thymic iNKT cell development. In this study, we demonstrated that ID2 and ID3 redundantly promoted iNKT cell lineage specification involving the induction of the signature transcription factor PLZF and that ID3 was critical for development of TBET-dependent NKT1 cells. In contrast, both ID2 and ID3 limited iNKT cell numbers by enforcing the postselection checkpoint in conventional thymocytes. Therefore, iNKT cells show both adaptive and innate-like requirements for ID proteins at distinct checkpoints during iNKT cell development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
E and Id proteins influence invariant NKT cell sublineage differentiation and proliferation.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 1;192(5):2227-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302904. Epub 2014 Jan 27. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24470501 Free PMC article.
-
Id3 and Id2 act as a dual safety mechanism in regulating the development and population size of innate-like γδ T cells.J Immunol. 2014 Feb 1;192(3):1055-1063. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302694. Epub 2013 Dec 30. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24379125 Free PMC article.
-
Combined deletion of Id2 and Id3 genes reveals multiple roles for E proteins in invariant NKT cell development and expansion.J Immunol. 2013 Nov 15;191(10):5052-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301252. Epub 2013 Oct 11. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24123680 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage Differentiation Program of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells.Immune Netw. 2017 Dec;17(6):365-377. doi: 10.4110/in.2017.17.6.365. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Immune Netw. 2017. PMID: 29302250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcriptional programs of iNKT cells.Semin Immunol. 2015 Feb;27(1):26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Semin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25841627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Id2 Collaborates with Id3 To Suppress Invariant NKT and Innate-like Tumors.J Immunol. 2017 Apr 15;198(8):3136-3148. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601935. Epub 2017 Mar 3. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28258199 Free PMC article.
-
Id2 regulates hyporesponsive invariant natural killer T cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;94(7):640-5. doi: 10.1038/icb.2016.19. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26880074 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestration of invariant natural killer T cell development by E and Id proteins.Crit Rev Immunol. 2015;35(1):33-48. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2015012207. Crit Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25746046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ILC Differentiation in the Thymus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1365:25-39. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8387-9_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35567739
-
Development of mucosal-associated invariant T cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2018 Jul;96(6):598-606. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12039. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Immunol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29569752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

