Immunomodulatory effects in a phase II study of lenalidomide combined with cetuximab in refractory KRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 24244687
- PMCID: PMC3823649
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080437
Immunomodulatory effects in a phase II study of lenalidomide combined with cetuximab in refractory KRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
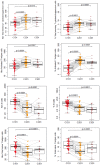
This study assessed the immunomodulatory effects in previously treated KRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer patients participating in a phase II multicenter, open-label clinical trial receiving lenalidomide alone or lenalidomide plus cetuximab. The main findings show the T cell immunostimulatory properties of lenalidomide as the drug induced a decrease in the percentage CD45RA(+) naïve T cells 3-fold while increasing the percentage HLA-DR(+) activated T helper cells and percentage total CD45RO(+) CD8(+) memory T cytotoxic cells, 2.6- and 2.1-fold respectively (p<0.0001). In addition, lenalidomide decreased the percentage of circulating CD19(+) B cells 2.6-fold (p<0.0001). Lenalidomide increased a modest, yet significant, 1.4-fold change in the percentage of circulating natural killer cells. Our findings indicate that lenalidomide significantly activates T cells, suggestive of an immunotherapeutic role for this drug in settings of maintenance therapy and tumor immunity. Furthermore, reported for the first time is the effect of lenalidomide in combination with cetuximab on T cell function, including increases in circulating naïve and central memory T cells. In summary, lenalidomide and cetuximab have significant effects on circulating immune cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01032291.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ito T, Ando H, Suzuki T, Ogura T, Hotta K, et al. (2010) Identification of a primary target of thalidomide teratogenicity. Science 327: 1345–1350. - PubMed
-
- Corral LG, Haslett PA, Muller GW, Chen R, Wong LM, et al. (1999) Differential cytokine modulation and T cell activation by two distinct classes of thalidomide analogues that are potent inhibitors of TNF-alpha. J Immunol 163: 380–386. - PubMed
-
- Schafer PH, Gandhi AK, Loveland MA, Chen RS, Man HW, et al. (2003) Enhancement of cytokine production and AP-1 transcriptional activity in T cells by thalidomide-related immunomodulatory drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305: 1222–1232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

