Adipokines, inflammation, insulin resistance, and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 24245495
- PMCID: PMC3978659
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4384
Adipokines, inflammation, insulin resistance, and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality are increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Inflammation is thought to be an important factor in accelerated atherosclerosis in RA, whereas insulin resistance is a known risk factor for atherosclerosis in RA. We hypothesised that adipokines could be a link between inflammation, insulin resistance, and atherosclerosis in RA.
Methods: The common carotid artery (CCA) intima-media thickness (IMT), CCA resistive index (RI), and carotid plaques were measured by ultrasonography in 192 patients with RA. Insulin resistance was assessed by the homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Serum adiponectin, leptin, resistin, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin (IL)-6 concentrations were determined.
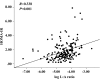
Results: The CCA RI was associated with CCA IMT and the estimated total plaque volume after adjustment for conventional CV risk factors. Among adipokines, resistin and IL-6 were correlated with inflammatory parameters. Leptin and leptin:adiponectin (L:A) ratio were correlated with metabolic risk factors, including HOMA-IR. And L:A ratio was related to the CCA RI after adjustment for conventional and nonconventional CV risk factors, including HOMA-IR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein.
Conclusion: L:A ratio was associated with HOMA-IR and carotid RI. L:A ratio might be an independent factor for predicting cardiovascular risk in patients with RA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response to 'Adipokines, inflammation, insulin resistance, and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis'.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Feb 10;16(1):401. doi: 10.1186/ar4478. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24507828 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Towards the elucidation of the true impact of adipocytokines on cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):127. doi: 10.1186/ar4412. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24611178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Del Rincon ID, Williams K, Stern MP, Freeman GL, Escalante A. High incidence of cardiovascular events in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort not explained by traditional cardiac risk factors. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;15:2737–2745. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200112)44:12<2737::AID-ART460>3.0.CO;2-#. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dessein PH, Joffe BI, Veller MG, Stevens BA, Tobias M, Reddi K, Stanwix AE. Traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors are associated with atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005;15:435–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

