Comorbidity between major depression and alcohol use disorder from adolescence to adulthood
- PMID: 24246605
- PMCID: PMC4131538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.10.007
Comorbidity between major depression and alcohol use disorder from adolescence to adulthood
Abstract
Background: Limited information exists regarding the long-term development of comorbidity between Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD; abuse/dependence). Using a representative prospective study, we examine multiple aspects pertaining to MDD+AUD comorbidity, with a focus on the relation between disorders across periods (adolescence, early adulthood, adulthood) and cumulative impairments by age 30.
Method: 816 participants were diagnostically interviewed at ages 16, 17, 24, and 30.
Results: Rates of comorbid MDD+AUD were low in adolescence (2%), but increased in early adulthood (11%) and adulthood (7%). Rates of cumulative comorbidity were elevated (21%). Most individuals with a history of MDD or AUD had the other disorder, except for women with MDD. Prospectively, adolescent AUD predicted early adult MDD, while early adult MDD predicted adult AUD. Compared to pure disorders, MDD+AUD was associated with higher risk of alcohol dependence, suicide attempt, lower global functioning, and life dissatisfaction.
Conclusions: Lifetime rates of comorbid MDD+AUD were considerably higher than in cross-sectional studies. Comorbidity was partly explained by bidirectional and developmentally-specific associations and predicted selected rather than generalized impairments. Clinically, our findings emphasize the need to always carefully assess comorbidity in patients with MDD or AUD, taking into account concurrency and developmental timing.
© 2014.
Figures
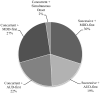
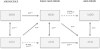
Similar articles
-
Depressed patients with co-occurring alcohol use disorders: a unique patient population.J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 Jun;69(6):907-15. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v69n0604. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18422397
-
Comorbidity of Lifetime Alcohol Use Disorder and Major Depressive Disorder in San Juan, Puerto Rico.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2019 Sep;80(5):546-551. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2019.80.546. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31603756 Free PMC article.
-
Physical and sexual abuse, depression and alcohol use disorders in adolescents: onsets and outcomes.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2003 Jan 24;69(1):51-60. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(02)00254-5. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2003. PMID: 12536066
-
Comorbid social anxiety disorder in patients with alcohol use disorder: A systematic review.J Psychiatr Res. 2018 Nov;106:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Psychiatr Res. 2018. PMID: 30236640
-
Psychedelic Research for Alcohol Use Disorder with Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder: An Unmet Need.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024 Dec;26(12):832-842. doi: 10.1007/s11920-024-01567-4. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024. PMID: 39612154 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of a digital alcohol moderation intervention as an add-on to depression treatment for young adults: study protocol of a multicentre pragmatic randomized controlled trial.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 May 22;21(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03222-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34022840 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying trajectories of alcohol use in a sample of secondary school students in Ontario and Alberta: longitudinal evidence from the COMPASS study.Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can. 2019 Sep;39(8-9):244-253. doi: 10.24095/hpcdp.39.8/9.02. Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can. 2019. PMID: 31517467 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol use disorder, psychiatric comorbidities, marriage and divorce in a high-risk sample.Psychol Addict Behav. 2022 Jun;36(4):364-374. doi: 10.1037/adb0000840. Epub 2022 May 26. Psychol Addict Behav. 2022. PMID: 35617219 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary evidence that individuals with remitted alcohol use disorder and major depressive disorder exhibit enhanced neural responses to reward: An EEG study.Addict Behav. 2023 Aug;143:107712. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2023.107712. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Addict Behav. 2023. PMID: 37028135 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the role of psychological distress in linking childhood maltreatment and alcohol use in young adulthood.Am J Addict. 2015 Oct;24(7):628-36. doi: 10.1111/ajad.12276. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Am J Addict. 2015. PMID: 26346173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boschloo L, Vogelzangs N, Smit JH, van den Brink W, Veltman DJ, Beekman AT, et al. Comorbidity and risk indicators for alcohol use disorders among persons with anxiety and/or depressive disorders: findings from the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA) J Affect Disord. 2011;131(1-3):233–42. - PubMed
-
- Grant BF, Harford TC. Comorbidity between DSM-IV alcohol use disorders and major depression: results of a national survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1995;39(3):197–206. - PubMed
-
- Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(7):830–42. - PubMed
-
- Cornelius JR, Salloum IM, Mezzich J, Cornelius MD, Fabrega H, Jr, Ehler JG, et al. Disproportionate suicidality in patients with comorbid major depression and alcoholism. Am J Psychiatry. 1995;152(3):358–64. - PubMed
-
- Schuckit MA. The clinical implications of primary diagnostic groups among alcoholics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985;42(11):1043–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

