Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cif protein enhances the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) and reduces major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen presentation
- PMID: 24247241
- PMCID: PMC3879540
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.459271
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cif protein enhances the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) and reduces major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen presentation
Abstract
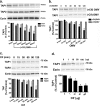
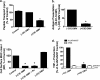
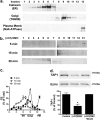
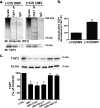
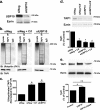
Cif (PA2934), a bacterial virulence factor secreted in outer membrane vesicles by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, increases the ubiquitination and lysosomal degradation of some, but not all, plasma membrane ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC), including the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and P-glycoprotein. The goal of this study was to determine whether Cif enhances the ubiquitination and degradation of the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP1 and TAP2), members of the ABC transporter family that play an essential role in antigen presentation and intracellular pathogen clearance. Cif selectively increased the amount of ubiquitinated TAP1 and increased its degradation in the proteasome of human airway epithelial cells. This effect of Cif was mediated by reducing USP10 deubiquitinating activity, resulting in increased polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of TAP1. The reduction in TAP1 abundance decreased peptide antigen translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum, an effect that resulted in reduced antigen available to MHC class I molecules for presentation at the plasma membrane of airway epithelial cells and recognition by CD8(+) T cells. Cif is the first bacterial factor identified that inhibits TAP function and MHC class I antigen presentation.
Keywords: ABC Transporter; Airway Epithelial Cell; Antigen Processing; Deubiquitination; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; TAP; Ubiquitination; Viral-Bacterial Co-infection.
Figures

References
-
- Swiatecka-Urban A., Moreau-Marquis S., Maceachran D. P., Connolly J. P., Stanton C. R., Su J. R., Barnaby R., O'Toole G. A., Stanton B. A. (2006) Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits endocytic recycling of CFTR in polarized human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 290, C862–C872 - PubMed
-
- MacEachran D. P., Ye S., Bomberger J. M., Hogan D. A., Swiatecka-Urban A., Stanton B. A., O'Toole G. A. (2007) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa secreted protein PA2934 decreases apical membrane expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Infect. Immun. 75, 3902–3912 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson T. M., Donaldson G. C., Johnston S. L., Openshaw P. J., Wedzicha J. A. (2006) Respiratory syncytial virus, airway inflammation, and FEV1 decline in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 173, 871–876 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

