Bioengineered Chinese hamster ovary cells with Golgi-targeted 3-O-sulfotransferase-1 biosynthesize heparan sulfate with an antithrombin-binding site
- PMID: 24247246
- PMCID: PMC3873583
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.519033
Bioengineered Chinese hamster ovary cells with Golgi-targeted 3-O-sulfotransferase-1 biosynthesize heparan sulfate with an antithrombin-binding site
Abstract
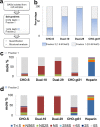
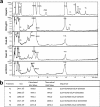
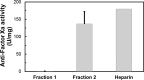
HS3st1 (heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase isoform-1) is a critical enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the antithrombin III (AT)-binding site in the biopharmaceutical drug heparin. Heparin is a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan that shares a common biosynthetic pathway with heparan sulfate (HS). Although only granulated cells, such as mast cells, biosynthesize heparin, all animal cells are capable of biosynthesizing HS. As part of an effort to bioengineer CHO cells to produce heparin, we previously showed that the introduction of both HS3st1 and NDST2 (N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase isoform-2) afforded HS with a very low level of anticoagulant activity. This study demonstrated that untargeted HS3st1 is broadly distributed throughout CHO cells and forms no detectable AT-binding sites, whereas Golgi-targeted HS3st1 localizes in the Golgi and results in the formation of a single type of AT-binding site and high anti-factor Xa activity (137 ± 36 units/mg). Moreover, stable overexpression of HS3st1 also results in up-regulation of 2-O-, 6-O-, and N-sulfo group-containing disaccharides, further emphasizing a previously unknown concerted interplay between the HS biosynthetic enzymes and suggesting the need to control the expression level of all of the biosynthetic enzymes to produce heparin in CHO cells.
Keywords: Antithrombin; Golgi; Heparan Sulfate; Heparin; Metabolic Engineering; Sulfotransferase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic engineering of Chinese hamster ovary cells: towards a bioengineered heparin.Metab Eng. 2012 Mar;14(2):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Metab Eng. 2012. PMID: 22326251 Free PMC article.
-
Lowered expression of heparan sulfate/heparin biosynthesis enzyme N-deacetylase/n-sulfotransferase 1 results in increased sulfation of mast cell heparin.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 30;286(52):44433-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.303891. Epub 2011 Nov 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22049073 Free PMC article.
-
The biosynthesis of anticoagulant heparan sulfate by the heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase isoform 5.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 17;1671(1-3):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2003.12.010. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15026143
-
Heparan sulfate and development: differential roles of the N-acetylglucosamine N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase isozymes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Dec 19;1573(3):209-15. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00386-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12417402 Review.
-
Mice deficient in heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase-1: normal hemostasis with unexpected perinatal phenotypes.Glycoconj J. 2002 May-Jun;19(4-5):355-61. doi: 10.1023/A:1025377206600. Glycoconj J. 2002. PMID: 12975616 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioengineered heparins and heparan sulfates.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Feb 1;97:237-49. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26555370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative HILIC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis of Glycosaminoglycans and Non-reducing End Carbohydrate Biomarkers via Glycan Reductive Isotopic Labeling.Anal Chem. 2025 Aug 19;97(32):17490-17500. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c02338. Epub 2025 Aug 6. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40767435 Free PMC article.
-
Can we produce heparin/heparan sulfate biomimetics using "mother-nature" as the gold standard?Molecules. 2015 Mar 5;20(3):4254-76. doi: 10.3390/molecules20034254. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25751786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted Heparin: Diverse Applications beyond Anticoagulant Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;17(10):1362. doi: 10.3390/ph17101362. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the role of 3-O-sulfotransferase in heparan sulfate biosynthesis.Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Aug 16;15(32):6792-6799. doi: 10.1039/c7ob01533j. Org Biomol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28770943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dreyfuss J. L., Regatieri C. V., Jarrouge T. R., Cavalheiro R. P., Sampaio L. O., Nader H. B. (2009) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: structure, protein interactions and cell signaling. An. Academ. Bras. Cienc. 81, 409–429 - PubMed
-
- Carlsson P., Kjellén L. (2012) Heparin biosynthesis. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 207, 23–41 - PubMed
-
- Esko J. D., Zhang L. (1996) Influence of core protein sequence on glycosaminoglycan assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6, 663–670 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

