Inhibition of CSF-1 receptor improves the antitumor efficacy of adoptive cell transfer immunotherapy
- PMID: 24247719
- PMCID: PMC3947337
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1816
Inhibition of CSF-1 receptor improves the antitumor efficacy of adoptive cell transfer immunotherapy
Abstract
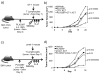
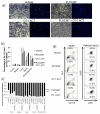
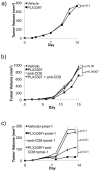
Colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) recruits tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIM) that suppress tumor immunity, including M2 macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC). The CSF-1 receptor (CSF-1R) is a tyrosine kinase that is targetable by small molecule inhibitors such as PLX3397. In this study, we used a syngeneic mouse model of BRAF(V600E)-driven melanoma to evaluate the ability of PLX3397 to improve the efficacy of adoptive cell therapy (ACT). In this model, we found that combined treatment produced superior antitumor responses compared with single treatments. In mice receiving the combined treatment, a dramatic reduction of TIMs and a skewing of MHCII(low) to MHCII(hi) macrophages were observed. Furthermore, mice receiving the combined treatment exhibited an increase in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) and T cells, as revealed by real-time imaging in vivo. In support of these observations, TILs from these mice released higher levels of IFN-γ. In conclusion, CSF-1R blockade with PLX3397 improved the efficacy of ACT immunotherapy by inhibiting the intratumoral accumulation of immunosuppressive macrophages.
Figures




References
-
- Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331:1565–1570. - PubMed
-
- Priceman SJ, Sung JL, Shaposhnik Z, Burton JB, Torres-Collado AX, Moughon DL, Johnson M, Lusis AJ, Cohen DA, Iruela-Arispe ML, et al. Targeting distinct tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells by inhibiting CSF-1 receptor: combating tumor evasion of antiangiogenic therapy. Blood. 2010;115:1461–1471. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tarhini AA, Butterfield LH, Shuai Y, Gooding WE, Kalinski P, Kirkwood JM. Differing patterns of circulating regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in metastatic melanoma patients receiving anti-CTLA4 antibody and interferon-alpha or TLR-9 agonist and GM-CSF with peptide vaccination. J Immunother. 2012;35:702–710. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

