Cardiac structure and function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: baseline findings from the echocardiographic study of the Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist trial
- PMID: 24249049
- PMCID: PMC4467731
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000887
Cardiac structure and function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: baseline findings from the echocardiographic study of the Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist trial
Abstract
Background: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. Existing data on cardiac structure and function in HFpEF suggest significant heterogeneity in this population.
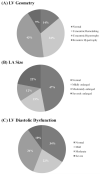
Methods and results: Echocardiograms were obtained from 935 patients with HFpEF (left ventricular ejection fraction ≥45%) enrolled in the Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist (TOPCAT) trial before initiation of randomized therapy. Average age was 70±10 years, 49% were women, 14% were of African descent, and comorbidities were highly prevalent. Centralized quantitative analysis in a blinded core laboratory demonstrated a mean left ventricular ejection fraction of 59.3±7.9%, with prevalent concentric left ventricular remodeling (34%) and hypertrophy (43%), and left atrial enlargement (53%). Diastolic dysfunction was present in 66% of gradable participants and was significantly associated with greater left ventricular hypertrophy and a higher prevalence of left atrial enlargement. Doppler evidence of pulmonary hypertension was present in 36%. At least 1 measure of structural heart disease was present in 93% of patients.
Conclusions: Patients enrolled in TOPCAT demonstrated heterogeneous patterns of ventricular remodeling, with high prevalence of structural heart disease, including left ventricular hypertrophy and left atrial enlargement, in addition to pulmonary hypertension, each of which has been associated with adverse outcomes in HFpEF. Diastolic function was normal in approximately one third of gradable participants, highlighting the heterogeneity of the cardiac phenotype in this syndrome. These findings deepen our understanding of the TOPCAT trial population and expand our knowledge of the diversity of the cardiac phenotype in HFpEF.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00094302.
Keywords: diastolic heart failure; echocardiography; heart failure; randomized controlled trial; spironolactone.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatia RS, Tu JV, Lee DS, Austin PC, Fang J, Haouzi A, Gong Y, Liu P. Outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a population-based study. New Engl J Med. 2006;355:260–9. - PubMed
-
- Owan TE, Hodge DO, Herges RM, Jacobsen SJ, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Trends in prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. New Engl J Med. 2006;355:251–9. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, Granger CB, Held P, McMurray JJV, Michelson EL, Olofsson B, Ostergren J, for the CHARM investigators and committees Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved left-ventricular ejection fraction: the CHARM-Preserved Trial. Lancet. 2003;362:777–81. - PubMed
-
- Cleland JGF, Tendera M, Adamus J, Freemantle N, Polonski L, Taylor J, on behalf of PEP-CHF investigators The perindopril in elderly people with chronic heart failure (PEP-CHF) study. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:2338–45. - PubMed
-
- Massie BM, Carson PE, McMurray JJ, Komajda M, McKelvie R, Zile MR, Anderson S, Donovan M, Iverson E, Staiger C, Ptaszynska A, for the I-PRESERVE investigators New Engl J Med. 2008;359:2456–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical