Efficacy and Safety of Terbinafine Hydrochloride 1% Cream vs. Sertaconazole Nitrate 2% Cream in Tinea Corporis and Tinea Cruris: A Comparative Therapeutic Trial
- PMID: 24249898
- PMCID: PMC3827518
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.119958
Efficacy and Safety of Terbinafine Hydrochloride 1% Cream vs. Sertaconazole Nitrate 2% Cream in Tinea Corporis and Tinea Cruris: A Comparative Therapeutic Trial
Abstract
Context: To the best of our knowledge, till date no study comparing the efficacy and safety of terbinafine hydrochloride 1% cream and sertaconazole nitrate 2% cream has been done in localized tinea corporis and tinea cruris.
Aims: This clinical trial was carried out to study and compare the efficacy of topical terbinafine hydrochloride 1% cream and sertaconazole nitrate 2% cream in localized tinea corporis and tinea cruris and to know the adverse effects of these antifungal creams.
Settings and design: In this prospective, single blind, randomized control trial with two arms, patient were randomized into two groups Group A (treatment with terbinafine cream) and Group B (treatment with sertaconazole cream). A total of 38 patients were enrolled for the study, 20 patients in group A and 18 patients in group B. But five patients of group A and three patients of group B were lost for follow-ups. Therefore sample size was of 30 patients with 15 patients in group A and group B each.
Materials and methods: Patients in group A and B were treated with twice daily topical 1% terbinafine hydrochloride and 2% sertaconazole nitrate cream respectively for a total duration of three weeks. Clinical improvement in signs and symptoms of each clinical parameter, namely itching, erythema, papules, pustules, vesicles, and scaling were graded weekly and clinical cure was assessed. KOH mount and culture was done weekly up to 3 weeks to access mycological cure. Fungal culture was done on Sabouraud's dextrose agar with chloramphenicol and cycloheximide.
Statistical analysis used: Statistical analysis was done using students paired and unpaired t-tests from the data obtained.
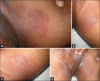
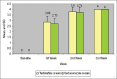
Results: Comparison between Group A and Group B for complete cure (clinical and mycological) showed that at the end of 3 weeks both terbinafine and sertaconazole groups had 100% complete cure. When the two groups were compared for complete cure, at the end of 1(st) and 2(nd) week, statistically non-significant results were observed (P = 0.461 and P = 0.679 respectively). However, at the end of 2(nd) week, complete cure rate for terbinafine was 80% as compared to 73.35% for sertaconazole with no statistical significance. In both Group A and Group B, clinically significant local side effects like erythema, swelling, stinging sensation, or increased itching were not noticed. A majority of our patients in both the group showed Trichophyton rubrum followed by Trichophyton mentagrophytes growth on culture. In Group A, 11 patients showed growth of T. rubrum, 2 patients showed growth of T. mentagrophytes, and 1 patient had only KOH test positive. In Group B, 10 patients revealed growth of T. rubrum, followed by growth of T. mentagrophytes in 3 and Microsporum canis in 2 patients. The therapeutic response is more or less same in infection with different species.
Conclusions: The newer fungistatic drug sertaconazole nitrate 2% cream was as effective as terbinafine hydrochloride 1% cream which is one of the fungicidal drugs, though terbinafine hydrochloride 1% cream has higher rates of complete cure at the end of 2 weeks as compared to sertaconazole nitrate 2% cream. Both the drugs showed good tolerability with no adverse effects.
Keywords: Dermatophytosis; sertaconazole nitrate 2% cream; terbinafine hydrochloride 1% cream.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of terbinafine hydrochloride 1% cream vs eberconazole nitrate 1% cream in localised tinea corporis and tinea cruris.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014 Apr;5(2):128-31. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.131079. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014. PMID: 24860743 Free PMC article.
-
Sertaconazole: a review of its use in the management of superficial mycoses in dermatology and gynaecology.Drugs. 2009;69(3):339-59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969030-00009. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19275277 Review.
-
Comparative assessment of the efficacy and safety of sertaconazole (2%) cream versus terbinafine cream (1%) versus luliconazole (1%) cream in patients with dermatophytoses: a pilot study.Indian J Dermatol. 2013 Jan;58(1):34-8. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.105284. Indian J Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23372210 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, double-blind trial of amorolfine 0.25% cream and sertaconazole 2% cream in limited dermatophytosis.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019 May-Jun;85(3):276-281. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_907_17. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019. PMID: 30409926 Clinical Trial.
-
Terbinafine. An update of its use in superficial mycoses.Drugs. 1999 Jul;58(1):179-202. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199958010-00018. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10439936 Review.
Cited by
-
New Antifungal Agents and New Formulations Against Dermatophytes.Mycopathologia. 2017 Feb;182(1-2):127-141. doi: 10.1007/s11046-016-0045-0. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Mycopathologia. 2017. PMID: 27502503 Review.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of topical sertaconazole versus topical terbinafine in localized dermatophytosis: A randomized, observer-blind, parallel group study.Indian J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov-Dec;48(6):659-664. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.194850. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 28066103 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A pilot single centre, double blind, placebo controlled, randomized, parallel study of Calmagen® dermaceutical cream and lotion for the topical treatment of tinea and onychomycosis.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Sep 18;17(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1970-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28923039 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment, prevention and public health management of impetigo, scabies, crusted scabies and fungal skin infections in endemic populations: a systematic review.Trop Med Int Health. 2019 Mar;24(3):280-293. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13198. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Trop Med Int Health. 2019. PMID: 30582783 Free PMC article.
-
Topical antifungal treatments for tinea cruris and tinea corporis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Aug 4;2014(8):CD009992. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009992.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25090020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niewerth M, Korting HC. The use of systemic antimycotics in dermatotherapy. Eur J Dermatol. 2000;10:155–60. - PubMed
-
- Suschka S, Fladung B, Merk HF. Clinical comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of once daily canesten with twice daily nizoral (clotrimazole1% cream vs. ketoconazole 2% cream) during a 28-day topical treatment of interdigital tinea pedis. Mycoses. 2002;45:91–6. - PubMed
-
- Croxtall JD, Plosker GL. Sertaconazole: A review of its use in the management of superficial mycoses in dermatology and gynaecology. Drugs. 2009;69:339–59. - PubMed
-
- Ryder NS. Terbinafine: Mode of action and properties of the squalene epoxidase inhibition. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:2–7. - PubMed
-
- Bonifaz A, Saúl A. Comparative study between terbinafine 1% emulsion-gel versus ketoconazole 2% cream in tinea cruris and tinea corporis. Eur J Dermatol. 2000;10:107–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
