Role of fluorine-18-labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography in the evaluation of axillary lymph node involvement in operable breast cancer in comparison with sentinel lymph node biopsy
- PMID: 24250021
- PMCID: PMC3822412
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-3919.119542
Role of fluorine-18-labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography in the evaluation of axillary lymph node involvement in operable breast cancer in comparison with sentinel lymph node biopsy
Abstract
Purpose: Role of (18 [F] fluorine-18-labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose [FDG] positron emission tomography-computed tomography [PET-CT]) in the evaluation of axillary lymph node involvement in T1T2N0 breast cancer and compare results with sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB).
Methods: A total of 37 patients of proven T1T2N0 breast cancer were included in the study. Patients with past history of breast surgery, T3T4 disease, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and pregnant patients were excluded from the study. Pre-operative FDG PET-CT was performed followed by sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy with blue dye or combined technique.
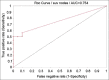
Results: SLN was identified in 32 of 37 patients with an identification rate of 86.48% (32/37). With combined technique SLN identification rate was 100% (6/6) while with blue dye alone; it was 83.8% (26/31). Among 37 patients, 16 had axillary metastases of which 12 had macrometastases and four had micrometastases detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Of 12 patients with axillary macrometastases, skip metastases were present in two patients in whom SLN was negative and in two patients SLN was not identified, but axillary dissection showed metastases. PET-CT had shown sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive value and positive predictive value of 56%, 90%, 73%, and 81.8%, respectively. IHC of SLN detected four patients with micrometastases upstaging the disease by 11% (4/37).
Conclusion: Because FDG PET-CT has a high specificity in the evaluation of axillary lymph node involvement in T1T2N0 breast cancer patients according to the results of this study if FDG PET-CT is positive in axillary lymph nodes, axillary lymph node dissection may be considered instead of SLNB.
Keywords: Breast cancer; fluorine-18-labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography; immunohistochemistry; sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Detection of Axillary Lymph Node Involvement in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Comparison between Staging 18F-2-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography Scans, Mammography, and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy.Indian J Nucl Med. 2023 Jul-Sep;38(3):249-254. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_183_22. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Indian J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 38046972 Free PMC article.
-
FDG-PET for axillary lymph node staging in primary breast cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004 Jun;31 Suppl 1:S97-102. doi: 10.1007/s00259-004-1531-z. Epub 2004 May 5. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004. PMID: 15133635 Review.
-
Assessment of axillary lymph node involvement in breast cancer patients with positron emission tomography using radiolabeled 2-(fluorine-18)-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Sep 4;88(17):1204-9. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.17.1204. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996. PMID: 8780629
-
Diagnostic value of sentinel lymph node scintigraphy and 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the detection of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with early-stage cervical cancer.World J Nucl Med. 2020 Jul 22;19(3):240-245. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_74_19. eCollection 2020 Jul-Sep. World J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 33354179 Free PMC article.
-
Sentinel lymph node as a new marker for therapeutic planning in breast cancer patients.J Surg Oncol. 2004 Mar;85(3):102-11. doi: 10.1002/jso.20022. J Surg Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14991881 Review.
Cited by
-
PET Molecular Imaging-Directed Biopsy: A Review.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017 Aug;209(2):255-269. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18047. Epub 2017 May 15. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017. PMID: 28504563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positron Emission Mammography (PEM) in the diagnosis of breast cancer: A systematic review and economic evaluation.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2020 Aug 18;34:100. doi: 10.34171/mjiri.34.100. eCollection 2020. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2020. PMID: 33315994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics of Sentinel Lymph Nodes in Early Breast Cancer for Identification of Thymidylate Synthase as a Potential Biomarker to Flag Metastasis: A Preliminary Study.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jun 23;12:4841-4854. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S255684. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32606973 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Axillary Lymph Node Involvement in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Comparison between Staging 18F-2-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography Scans, Mammography, and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy.Indian J Nucl Med. 2023 Jul-Sep;38(3):249-254. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_183_22. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Indian J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 38046972 Free PMC article.
-
18F-FDG PET/CT Semiquantitative and Radiomic Features for Assessing Pathologic Axillary Lymph Node Status in Clinical Stage I-III Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review.Curr Oncol. 2025 May 23;32(6):300. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32060300. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40558244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–30. - PubMed
-
- Walls J, Boggis CR, Wilson M, Asbury DL, Roberts JV, Bundred NJ, et al. Treatment of the axilla in patients with screen-detected breast cancer. Br J Surg. 1993;80:436–8. - PubMed
-
- Crane-Okada R, Wascher RA, Elashoff D, Giuliano AE. Long-term morbidity of sentinel node biopsy versus complete axillary dissection for unilateral breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:1996–2005. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

