Abnormal extraosseous activity in both lungs and stomach in pre-transplant 99mTc-MDP bone scan disappearing after renal transplant
- PMID: 24250025
- PMCID: PMC3822416
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-3919.119549
Abnormal extraosseous activity in both lungs and stomach in pre-transplant 99mTc-MDP bone scan disappearing after renal transplant
Abstract
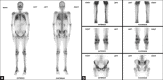
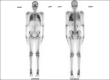
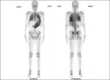
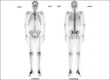
A chronic kidney disease male patient presenting with bone pains, fever, weakness, and clinically ascites was subjected to four technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate (Tc99m-MDP) bone scans, two before renal transplant and two after renal transplants. Pretransplant bone scan revealed metabolic bone disease with focal insufficiency fractures. Marked extraosseous activity in both lungs and stomach was also visualized. On regular hemodialysis (HD) after 4 months, repeat pretransplant bone scan showed persistent uptake in lungs and stomach, representing altered calcium metabolism with microcalcifications. He underwent human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matched live donor renal transplantation, started on immune-suppression and steroids. Posttransplant bone scan at 20 days revealed no definite interval change, but bone scan performed approximately 17 months posttransplant showed resolving metabolic bone disease and the tracer uptake in the lungs and stomach was no more visualized. Patient clinically followed-up until the date (February 2013) is asymptomatic with serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dl, no bone scan done.
Keywords: 99mTc-MDP; bone scan; chronic kidney disease; gastric uptake; hemodialysis; lung uptake.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extraosseous Accumulation of Technetium-99m-Methyl Diphosphonate (99mTc-MDP) in a Child with ALL: A Case Report.Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. 2018 Winter;6(1):57-60. doi: 10.22038/aojnmb.2017.9679. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29333468 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate characterization of 99mTc-MDP uptake in extraosseous neoplasm mimicking bone metastasis on whole-body bone scan: contribution of SPECT/CT.BMC Med Imaging. 2019 May 30;19(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12880-019-0345-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31146746 Free PMC article.
-
Technetium-99m-methylene Diphosphonate Uptake in Hepatic Necrosis Secondary to Respiratory Failure.World J Nucl Med. 2013 Sep;12(3):116-9. doi: 10.4103/1450-1147.136736. World J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 25165422 Free PMC article.
-
A report on the incidence of intestinal 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate uptake of bone scans and a review of the literature.Nucl Med Commun. 2006 Nov;27(11):877-85. doi: 10.1097/01.mnm.0000237991.44948.13. Nucl Med Commun. 2006. PMID: 17021428 Review.
-
SPECT-CT for characterization of extraosseous uptake of 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate on bone scintigraphy.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013 Sep-Oct;19(5):405-10. doi: 10.5152/dir.2013.054. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23748034 Review.
Cited by
-
An uncommon case showing three different pathologies on (99m)technetium-methylene diphosphonate bone scintigraphy.Indian J Nucl Med. 2015 Jan-Mar;30(1):80-1. doi: 10.4103/0972-3919.147555. Indian J Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 25589816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brill DR. Radionuclide imaging of nonneoplastic soft tissue disorders. Semin Nucl Med. 1981;11:277–88. - PubMed
-
- Rosenthal DI, Chandler HL, Azizi F, Schneider PB. Uptake of bone imaging agents by diffuse pulmonary metastatic calcification. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977;129:871–4. - PubMed
-
- Chan ED, Morales DV, Welsh CH, McDermott MT, Schwarz MI. Calcium deposition with or without bone formation in the lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1654–69. - PubMed
-
- Watson NW, Jr, Cowan RJ, Maynard CD, Richards F., 2nd Resolution of metastatic calcification revealed by bone scanning: Case report. J Nucl Med. 1977;18:890–2. - PubMed
-
- Delcourt E, Baudoux M, Neve P. Tc-99m-MDP bone scanning detection of gastric calcification. Clin Nucl Med. 1980;5:546–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

