Triology of nitric oxide, mast cell and stress in pathogenesis of oral lichen planus
- PMID: 24250071
- PMCID: PMC3830219
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.119741
Triology of nitric oxide, mast cell and stress in pathogenesis of oral lichen planus
Abstract
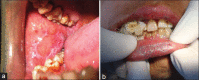
Introduction: Oral Lichen planus (OLP) is chronic, autoimmune, mucocutaneous disease. Numerous etiological factors have been proposed, but an authoritative and exact source of the disease has not been brought forward. Reactive nitrogen species (RNS), mast cell (MC) and stress are considered to play a key role in inflammation-mediated carcinogenesis generating nitric oxide (NO).
Aim: To evaluate the salivary NO levels, mast cells and stress levels and to correlate them in pathogenesis of OLP.
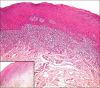
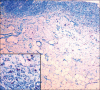
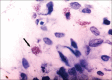
Materials and methods: The study was conducted using saliva samples of patients. The study consisted of two groups: Group-I constituted the subjects with OLP group (n=25) and group II comprised the control group (n=25). The saliva of the patients was evaluated using Griess Reagent and Spectrophotometer, MC count done by using special stains, and stress levels measured using DASS Scale.
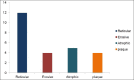
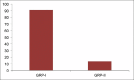
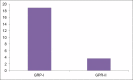
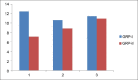
Results: The difference between the means was found to be highly significant (P < 0.05). The intergroup comparison of optical density (OD) values, a mast cell count and stress level was found to be highly significant.
Conclusion: Salivary NO, increase in mast cell count and stress has a definitive role in OLP pathogenesis.
Keywords: Depression anxiety stress scale; mast cells; oral lichen planus; salivary nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Markers in Oral Lichen Planus.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 27;2021:9914652. doi: 10.1155/2021/9914652. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34616506 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological status and uric acid levels in oral lichen planus patients - A case- control study.Indian J Dent Res. 2020 May-Jun;31(3):368-375. doi: 10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_289_19. Indian J Dent Res. 2020. PMID: 32769269
-
Salivary and serum estrogen level assessment in oral lichen planus patients and its correlative analysis with OLP and stress.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 May;13(5):1998-2005. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1332_23. Epub 2024 May 24. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38948558 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mast cells in pathogenesis of oral lichen planus.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2011 Sep;15(3):267-71. doi: 10.4103/0973-029X.86674. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2011. PMID: 22144827 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell expression in oral lichen planus: A systematic review.J Investig Clin Dent. 2019 Nov;10(4):e12457. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12457. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019. PMID: 31454180
Cited by
-
Erosive oral lichen planus inflicts higher cellular stress than reticular type.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2021 May-Aug;25(2):279-285. doi: 10.4103/0973-029X.325127. Epub 2021 Aug 31. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34703122 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Markers in Oral Lichen Planus.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 27;2021:9914652. doi: 10.1155/2021/9914652. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34616506 Free PMC article.
-
The role of vitamin D deficiency in the development and severity of oral lichen planus: a case-control study.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 May 30;29(6):320. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06398-y. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 40445356 Free PMC article.
-
Depressive Disorder and Dermatological Autoimmune Diseases.J Clin Med. 2024 May 30;13(11):3224. doi: 10.3390/jcm13113224. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38892934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Salivary Nitric Oxide Levels in Smokers, Tobacco Chewers and Patients with Oral Lichenoid Reactions.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Jan;10(1):ZC63-6. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/16517.7126. Epub 2016 Jan 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 26894179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ismail SB, Kumar SK, Zain RB. Oral lichen planus and lichenoid reactions: Etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, management and malignant transformation. J Oral Sci. 2007;49:89–106. - PubMed
-
- Mallaoglu N. Oral lichen planus: A review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;35:370–7. - PubMed
-
- Scully C, Beyli M, Ferreiro MC, Ficarra G, Gill Y, Griffiths M, et al. Update on oral lichen planus: Etiopathogenesis and management. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998;9:86–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

