Monostostic fibrous dysplasia with nonspecific cystic degeneration: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 24250093
- PMCID: PMC3830241
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.119765
Monostostic fibrous dysplasia with nonspecific cystic degeneration: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
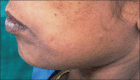
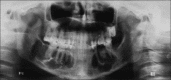
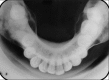
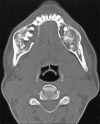
Fibrous dysplasia (FD) has been regarded as a developmental skeletal disorder characterized by replacement of normal bone with benign cellular fibrous connective tissue. It has now become evident that FD is a genetic disease caused by somatic activating mutation of the Gsα subunit of G protein-coupled receptor. Here we report a case of bilateral monostotic FD in a middle-aged female showing a classic histological picture, but radiologically presenting as a mixed radiolucent radiopaque lesion showing nonspecific cystic degeneration.
Keywords: Fibrous dysplasia; monostotic; nonspecific cystic degeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
An unusual presentation of non-specific cystic degeneration of craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: a case report and review of literature.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020 Sep 16;42(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40902-020-00275-2. eCollection 2020 Dec. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020. PMID: 32995343 Free PMC article.
-
Nonspecific Cystic Degeneration in Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia: A Rare Finding.Contemp Clin Dent. 2022 Jul-Sep;13(3):284-288. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_245_21. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Contemp Clin Dent. 2022. PMID: 36213857 Free PMC article.
-
The nature of fibrous dysplasia.Head Face Med. 2009 Nov 9;5:22. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-5-22. Head Face Med. 2009. PMID: 19895712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gsalpha gene mutations in monostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone and fibrous dysplasia-like low-grade central osteosarcoma.Virchows Arch. 2001 Aug;439(2):170-5. doi: 10.1007/s004280100453. Virchows Arch. 2001. PMID: 11561757
-
[Progresses in the study of fibrous dysplasia of the jaw bone].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2009 Oct;18(5):540-4. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2009. PMID: 19907865 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Office Three-Dimensional Printed Osteotomy Guide for Corrective Osteotomy in Fibrous Dysplasia.Cureus. 2023 Mar 20;15(3):e36384. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36384. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37090315 Free PMC article.
-
An unusual presentation of non-specific cystic degeneration of craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: a case report and review of literature.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020 Sep 16;42(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40902-020-00275-2. eCollection 2020 Dec. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020. PMID: 32995343 Free PMC article.
-
Monostotic craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: report of two cases with interesting histology.Autops Case Rep. 2019 Jun 11;9(2):e2018092. doi: 10.4322/acr.2018.092. eCollection 2019 Apr-Jun. Autops Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31321219 Free PMC article.
-
Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia with cystic degeneration - A diagnostic challenge.J Clin Exp Dent. 2023 Sep 1;15(9):e781-e786. doi: 10.4317/jced.60736. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Clin Exp Dent. 2023. PMID: 37799754 Free PMC article.
-
Giant monostotic osteofibrous dysplasia of the ilium: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2018 Nov 26;6(14):830-835. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.830. World J Clin Cases. 2018. PMID: 30510951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM. Oral maxillofacial pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2002. pp. 553–7.
-
- Ippolito E, Bray EW, Corsi A, De Maio F, Exner UG, Robey PG, et al. European Pediatric Orthopaedic Society. Natural history and treatment of fibrous dysplasia of bone: A multicenter clinicopathologic study promoted by the European Pediatric Orthopaedic Society. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2003;12:155–77. - PubMed
-
- Bessho K, Tagawa T, Murata M, Komaki M. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia with involvement of the mandibular canal. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989;68:396–400. - PubMed
-
- Di Caprio MR, Enneking WF. Fibrous dysplasia. Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1848–64. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

