Chemically cross-linked poly(acrylic-co-vinylsulfonic) acid hydrogel for the delivery of isosorbide mononitrate
- PMID: 24250265
- PMCID: PMC3821952
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/340737
Chemically cross-linked poly(acrylic-co-vinylsulfonic) acid hydrogel for the delivery of isosorbide mononitrate
Abstract
We report synthesis, characterization, and drug release attributes of a series of novel pH-sensitive poly(acrylic-co-vinylsulfonic) acid hydrogels. These hydrogels were prepared by employing free radical polymerization using ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) and benzyl peroxide (BPO) as cross-linker and initiator, respectively. Effect of acrylic acid (AA), polyvinylsulfonic acid (PVSA), and EGDMA on prepared hydrogels was investigated. All formulations showed higher swelling at high pHs and vice versa. Formulations containing higher content of AA and EGDMA show reduced swelling, but one with higher content of PVSA showed increased swelling. Hydrogel network was characterized by determining structural parameters and loaded with isosorbide mononitrate. FTIR confirmed absence of drug polymer interaction while DSC and TGA demonstrated molecular dispersion of drug in a thermally stable polymeric network. All the hydrogel formulations exhibited a pH dependent release of isosorbide mononitrate which was found to be directly proportional to pH of the medium and PVSA content and inversely proportional to the AA contents. Drug release data were fitted to various kinetics models. Results indicated that release of isosorbide mononitrate from poly(AA-co-VSA) hydrogels was non-Fickian and that the mechanism was diffusion-controlled.
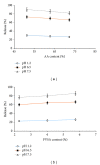
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate on swelling and on metformin hydrochloride release behavior of chemically crosslinked pH-sensitive acrylic acid-polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.Daru. 2015 Aug 19;23(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40199-015-0123-8. Daru. 2015. PMID: 26283081 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-linked pH-sensitive pectin and acrylic acid based hydrogels for controlled delivery of metformin.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020 Jul;33(4):1483-1491. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33583778
-
Preparation and characterization of hybrid pH-sensitive hydrogels of chitosan-co-acrylic acid for controlled release of verapamil.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010 Oct;21(10):2805-16. doi: 10.1007/s10856-010-4134-1. Epub 2010 Aug 5. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010. PMID: 20686825
-
Swelling behavior and morphological properties of semi-IPN hydrogels based on ionic and non-ionic components.Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(4):1725-33. doi: 10.3233/BME-140984. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014. PMID: 24948456
-
Isosorbide mononitrate 30% immediate-release 70% sustained-release formulation: a review. DUMQOL (DUtch Mononitrate Quality of Life) Study Group.Angiology. 2000 Aug;51(8):631-8. Angiology. 2000. PMID: 10959515 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in the application of hydrogels in immunotherapy of gastrointestinal tumors.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2161670. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2161670. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36587630 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and characterization of framycetin sulphate loaded hydrogel dressing for enhanced wound healing.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 17;20(4):e0317273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317273. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40244999 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing Radiation Crosslinked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Environmental Remediation.Gels. 2025 Jun 25;11(7):492. doi: 10.3390/gels11070492. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40710653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Crosslinked Hydrogels Comprising Poly(Vinylphosphonic Acid) and Bis[2-(Methacryloyloxy)Ethyl] Phosphate as an Efficient Adsorbent for Wastewater Dye Removal.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jan 10;10(1):131. doi: 10.3390/nano10010131. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936837 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(vinylphosphonic acid-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels: The effect of copolymer composition on osteoblast adhesion and proliferation.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018 Jan;106(1):255-264. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36234. Epub 2017 Oct 24. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018. PMID: 28891249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SJ, Park SJ, Kim SI. Properties of smart hydrogels composed of polyacrylic acid/poly(vinyl sulfonic acid) responsive to external stimuli. Smart Materials and Structures. 2004;13(2):317–322.
-
- Atta AM, Abdel-Azim A-AA. Effect of crosslinker functionality on swelling and network parameters of copolymeric hydrogels. Polymers for Advanced Technologies. 1998;9(6):340–348.
-
- Roy N, Saha N, Kitano T, Saha P. Novel hydrogels of PVP-CMC and their swelling effect on viscoelastic properties. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2010;117(3):1703–1710.
-
- Zhang J, Xie R, Zhang S-B, Cheng C-J, Ju X-J, Chu L-Y. Rapid pH/temperature-responsive cationic hydrogels with dual stimuli-sensitive grafted side chains. Polymer. 2009;50(11):2516–2525.
-
- Lo YL, Hsu CY, Lin HR. pH-and thermo-sensitive pluronic/poly(acrylic acid) in situ hydrogels for sustained release of an anticancer drug. Journal of Drug Targeting. 2013;21:54–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

