Alzheimer's disease risk assessment using large-scale machine learning methods
- PMID: 24250789
- PMCID: PMC3826736
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077949
Alzheimer's disease risk assessment using large-scale machine learning methods
Abstract
The goal of this work is to introduce new metrics to assess risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD) which we call AD Pattern Similarity (AD-PS) scores. These metrics are the conditional probabilities modeled by large-scale regularized logistic regression. The AD-PS scores derived from structural MRI and cognitive test data were tested across different situations using data from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) study. The scores were computed across groups of participants stratified by cognitive status, age and functional status. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to evaluate associations with the distribution of conversion times from mild cognitive impairment to AD. The performances of classifiers developed using data from different types of brain tissue were systematically characterized across cognitive status groups. We also explored the performance of anatomical and cognitive-anatomical composite scores generated by combining the outputs of classifiers developed using different types of data. In addition, we provide the AD-PS scores performance relative to other metrics used in the field including the Spatial Pattern of Abnormalities for Recognition of Early AD (SPARE-AD) index and total hippocampal volume for the variables examined.
Conflict of interest statement
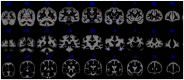
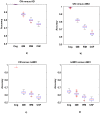
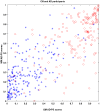
Figures

References
-
- Donoho D (2000) High-Dimensional Data Analysis: The Curses and Blessings of Dimensionality, Lecture on August 8,2000, To the American Mathematical Society ' Math Challenges of the 21st Century.”
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

