Topical Nitroglycerine for Neonatal Arterial Associated Peripheral Ischemia following Cannulation: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review
- PMID: 24251058
- PMCID: PMC3819912
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/608516
Topical Nitroglycerine for Neonatal Arterial Associated Peripheral Ischemia following Cannulation: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review
Abstract
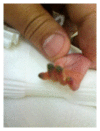
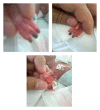
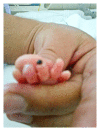
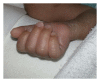
Arterial cannulation in neonates is usually performed for frequent blood pressure monitoring and blood sampling. The procedure, while easily executed by skilled neonatal staff, can be associated with serious complications such as vasospasm, thrombosis, embolism, hematoma, infection, peripheral nerve damage, ischemia, and tissue necrosis. Several treatment options are available to reverse vascular induced ischemia and tissue damage. Applied interventions depend on the extent of tissue involvement and whether the condition is progressive and deemed life threatening. Standard, noninvasive measures include immediate catheter removal, limb elevation, and warming the contralateral extremity. Topical vasodilators, anticoagulation, thrombolysis, and surgery are considered secondary therapeutic strategies. A comprehensive literature search indicates that topical nitroglycerin has been utilized for the treatment of tissue ischemia in three preterms with umbilical arterial catheters and four with peripheral arterial lines. We report the first successful use of nitroglycerine ointment in a critically ill preterm infant with ischemic hand changes after brachial artery cannulation.
Figures

References
-
- Massaro AN, Rais-Bahrami K, Eichelberger MR. Atlas of Procedures in Neonatology. 4th edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Wolters Kluwer. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007. (M. G. Macdoanld, J. Ramasethu, Eds., pp. 186–198).
-
- Newall F, Johnston L, Ignjatovic V, Monagle P. Unfractionated heparin therapy in infants and children. Pediatrics. 2009;123(3):e510–e518. - PubMed
-
- Michaels LA, Gurian M, Hegyi T, Drachtman RA. Low molecular weight heparin in the treatment of venous and arterial thromboses in the premature infant. Pediatrics. 2004;114(3):703–707. - PubMed
-
- Malowany JI, Monagle P, Knoppert DC, et al. Enoxaparin for neonatal thrombosis: a call for a higher dose for neonates. Thrombosis Research. 2008;122(6):826–830. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

