Toxin-antitoxin systems: Biology, identification, and application
- PMID: 24251069
- PMCID: PMC3827094
- DOI: 10.4161/mge.26219
Toxin-antitoxin systems: Biology, identification, and application
Abstract
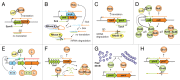
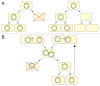
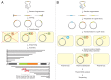
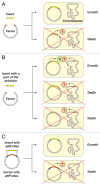
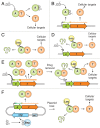
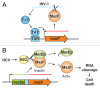
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems are small genetic elements composed of a toxin gene and its cognate antitoxin. The toxins of all known TA systems are proteins while the antitoxins are either proteins or non-coding RNAs. Based on the molecular nature of the antitoxin and its mode of interaction with the toxin the TA modules are currently grouped into five classes. In general, the toxin is more stable than the antitoxin but the latter is expressed to a higher level. If supply of the antitoxin stops, for instance under special growth conditions or by plasmid loss in case of plasmid encoded TA systems, the antitoxin is rapidly degraded and can no longer counteract the toxin. Consequently, the toxin becomes activated and can act on its cellular targets. Typically, TA toxins act on crucial cellular processes including translation, replication, cytoskeleton formation, membrane integrity, and cell wall biosynthesis. TA systems and their components are also versatile tools for a multitude of purposes in basic research and biotechnology. Currently, TA systems are frequently used for selection in cloning and for single protein expression in living bacterial cells. Since several TA toxins exhibit activity in yeast and mammalian cells they may be useful for applications in eukaryotic systems. TA modules are also considered as promising targets for the development of antibacterial drugs and their potential to combat viral infection may aid in controlling infectious diseases.
Keywords: RNA interferase; antitoxin; cloning; protein expression; toxin; translation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems: Classification, biological roles, and applications.Microbiol Res. 2022 Nov;264:127159. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127159. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Microbiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35969944 Review.
-
Applications of toxin-antitoxin systems in synthetic biology.Eng Microbiol. 2023 Jan 18;3(2):100069. doi: 10.1016/j.engmic.2023.100069. eCollection 2023 Jun. Eng Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 39629251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial toxin-antitoxin modules: classification, functions, and association with persistence.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2021 Jul 7;2:100047. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100047. eCollection 2021 Dec. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2021. PMID: 34841338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TasA-tasB, a new putative toxin-antitoxin (TA) system from Bacillus thuringiensis pGI1 plasmid is a widely distributed composite mazE-doc TA system.BMC Genomics. 2006 Oct 13;7:259. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-259. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 17038198 Free PMC article.
-
sRNAs in bacterial type I and type III toxin-antitoxin systems.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015 May;39(3):413-27. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv003. Epub 2015 Mar 25. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25808661 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomics-guided identification of a conserved CptBA-like toxin-antitoxin system in Acinetobacter baumannii.J Adv Res. 2020 Nov 23;30:159-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.11.007. eCollection 2021 May. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 34026293 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity proteins of dual nuclease T6SS effectors function as transcriptional repressors.EMBO Rep. 2021 Jun 4;22(6):e51857. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051857. Epub 2021 Mar 30. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33786997 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for Special Issue "Bacterial Toxin-Antitoxin Systems".Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 8;12(1):128. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010128. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38257955 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of phage-derived RNA-based technologies in synthetic biology.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;5(4):343-360. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2020.09.003. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33083579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One cannot rule them all: Are bacterial toxins-antitoxins druggable?FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015 Jul;39(4):522-40. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv002. Epub 2015 Mar 21. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25796610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
