Novel strategies for gene trapping and insertional mutagenesis mediated by Sleeping Beauty transposon
- PMID: 24251071
- PMCID: PMC3827069
- DOI: 10.4161/mge.26499
Novel strategies for gene trapping and insertional mutagenesis mediated by Sleeping Beauty transposon
Abstract
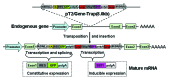
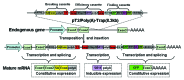
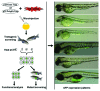
Gene and poly(A) trappings are high-throughput approaches to capture and interrupt the expression of endogenous genes within a target genome. Although a number of trapping vectors have been developed for investigation of gene functions in cells and vertebrate models, there is still room for the improvement of their efficiency and sensitivity. Recently, two novel trapping vectors mediated by Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon have been generated by the combination of three functional cassettes that are required for finding endogenous genes, disrupting the expression of trapped genes, and inducing the excision of integrated traps from their original insertion sites and then inserting into another gene. In addition, several other strategies are utilized to improve the activities of two trapping vectors. First, activities of all components were examined in vitro before the generation of two vectors. Second, the inducible promoter from the tilapia Hsp70 gene was used to drive the expression of SB gene, which can mediate the excision of integrated transposons upon induction at 37 °C. Third, the Cre/LoxP system was introduced to delete the SB expression cassette for stabilization of gene interruption and bio-safety. Fourth, three stop codons in different reading frames were introduced downstream of a strong splice acceptor (SA) in the gene trapping vector to effectively terminate the translation of trapped endogenous genes. Fifth, the strong splicing donor (SD) and AU-rich RNA-destabilizing element exhibited no obvious insertion bias and markedly reduced SD read-through events, and the combination of an enhanced SA, a poly(A) signal and a transcript terminator in the poly(A) trapping vector efficiently disrupted the transcription of trapped genes. Thus, these two trapping vectors are alternative and effective tools for large-scale identification and disruption of endogenous genes in vertebrate cells and animals.
Keywords: Sleeping Beauty; gene trapping; insertional mutagenesis; poly(A) trapping; transposon.
Figures
Comment on
- Song G, Li Q, Long Y, Gu Q, Hackett PB, Cui Z. Effective gene trapping mediated by Sleeping Beauty transposon. PLoS One. 2012;7:e44123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044123
- Song G, Li Q, Long Y, Hackett PB, Cui Z. Effective expression-independent gene trapping and mutagenesis mediated by Sleeping Beauty transposon. J Genet Genomics. 2012;39:503–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.05.010. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.05.010
References
-
- Driever W, Solnica-Krezel L, Schier AF, Neuhauss SC, Malicki J, Stemple DL, Stainier DY, Zwartkruis F, Abdelilah S, Rangini Z, et al. A genetic screen for mutations affecting embryogenesis in zebrafish. Development. 1996;123:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Haffter P, Granato M, Brand M, Mullins MC, Hammerschmidt M, Kane DA, Odenthal J, van Eeden FJ, Jiang YJ, Heisenberg CP, et al. The identification of genes with unique and essential functions in the development of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development. 1996;123:1–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
