Familial vitamin D resistant rickets: End-organ resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
- PMID: 24251166
- PMCID: PMC3830312
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.119579
Familial vitamin D resistant rickets: End-organ resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
Abstract
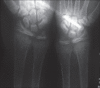
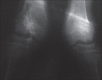
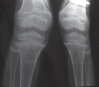
Rickets is softening of bones due to defective mineralization of cartilage in the epiphyseal growth plate, leading to widening of ends of long bones, growth retardation, and skeletal deformities in children. The predominant cause is deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D. The observation that some forms of rickets could not be cured by regular doses of vitamin D, led to the discovery of rare inherited abnormalities of vitamin D metabolism or vitamin D receptor. Vitamin D dependent rickets (VDDR) is of two types: Type I is due to defective renal tubular 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1-α hydroxylase and type II is due to end-organ resistance to active metabolite of vitamin D. Typical signs are observed from the first month of life. The patient with rickets described below had markedly increased serum alkaline phosphatase and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. We attribute these abnormalities to impaired end-organ responsiveness to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D.
Keywords: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; End-organ resistance; rickets; vitamin D; vitamin D dependent rickets.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Albright F, Butler AM, Bloomberg E. Rickets resistant to vitamin D therapy. AJDC. 1937;54:529–47.
-
- Fraher LJ, Karmali R, Hinde FR, Hendy GN, Jani H, Nicholson L, et al. Vitamin D-dependent rickets type II: Extreme end organ resistant to 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D 3 in a patient without alopecia. Eur J Pediatr. 1986;145:389–95. - PubMed
-
- Lips P. Vitamin D related disorders in primer on the metabolic bone disease and disorders of mineral metabolism. In: Rosen CJ, et al., editors. 7th ed. Washington: ASBMR; pp. 329–35.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

