GLYX-13, an NMDA receptor glycine site functional partial agonist enhances cognition and produces antidepressant effects without the psychotomimetic side effects of NMDA receptor antagonists
- PMID: 24251380
- PMCID: PMC4721220
- DOI: 10.1517/13543784.2014.852536
GLYX-13, an NMDA receptor glycine site functional partial agonist enhances cognition and produces antidepressant effects without the psychotomimetic side effects of NMDA receptor antagonists
Abstract
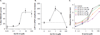
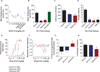
Introduction: The N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-ionophore complex plays a key role in learning and memory and has efficacy in animals and humans with affective disorders. GLYX-13 is an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) glycine-site functional partial agonist and cognitive enhancer that also shows rapid antidepressant activity without psychotomimetic side effects.
Areas covered: The authors review the mechanism of action of GLYX-13 that was investigated in preclinical studies and evaluated in clinical studies. Specifically, the authors review its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and drug safety that were demonstrated in clinical studies.
Expert opinion: NMDAR full antagonists can produce rapid antidepressant effects in treatment-resistant subjects; however, they are often accompanied by psychotomimetic effects that make chronic use outside of a clinical trial inpatient setting problematic. GLYX-13 appears to exert its antidepressant effects in the frontal cortex via NMDAR-triggered synaptic plasticity. Understanding the mechanistic underpinning of GLYX-13's antidepressant action should provide both novel insights into the role of the glutamatergic system in depression and identify new targets for therapeutic development.
Figures
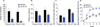
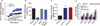
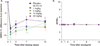
References
-
-
Paoletti P, Bellone C, Zhou Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14(6):383–400. •• Most recent review of biochemical pharmacological and physiological properties of known NMDA receptor subtypes: the future of NMDA receptor drug discovery programs will evolve to address receptor subtype specific disease modulation.
-
-
- Monyer H, Burnashev N, Laurie DJ, et al. Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron. 1994;12(3):529–540. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Sakimura K, Mishina M. Developmental changes in distribution of NMDA receptor channel subunit mRNAs. Neuroreport. 1992;3(12):1138–1140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
