Regulation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by vascular smooth muscle hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- PMID: 24251580
- PMCID: PMC3977726
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201302-0302OC
Regulation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by vascular smooth muscle hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
Abstract
Rationale: Chronic hypoxia induces pulmonary vascular remodeling, pulmonary hypertension, and right ventricular hypertrophy. At present, little is known about mechanisms driving these responses. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a master regulator of transcription in hypoxic cells, up-regulating genes involved in energy metabolism, proliferation, and extracellular matrix reorganization. Systemic loss of a single HIF-1α allele has been shown to attenuate hypoxic pulmonary hypertension, but the cells contributing to this response have not been identified.
Objectives: We sought to determine the contribution of HIF-1α in smooth muscle on pulmonary vascular and right heart responses to chronic hypoxia.
Methods: We used mice with homozygous conditional deletion of HIF-1α combined with tamoxifen-inducible smooth muscle-specific Cre recombinase expression. Mice received either tamoxifen or vehicle followed by exposure to either normoxia or chronic hypoxia (10% O2) for 30 days before measurement of cardiopulmonary responses.
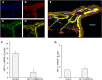
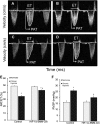
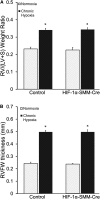
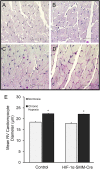
Measurements and main results: Tamoxifen-induced smooth muscle-specific deletion of HIF-1α attenuated pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension in chronic hypoxia. However, right ventricular hypertrophy was unchanged despite attenuated pulmonary pressures.
Conclusions: These results indicate that HIF-1α in smooth muscle contributes to pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension in chronic hypoxia. However, loss of HIF-1 function in smooth muscle does not affect hypoxic cardiac remodeling, suggesting that the cardiac hypertrophy response is not directly coupled to the increase in pulmonary artery pressure.
Figures


Comment in
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells and hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Feb 1;189(3):245-6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201312-2148ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24484328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Strange C, Highland KB. Pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2005;11:452–455. - PubMed
-
- Roy R, Couriel JM. Secondary pulmonary hypertension. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2006;7:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Stenmark KR, Abman SH. Lung vascular development: implications for the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:623–661. - PubMed
-
- Naeije R. Pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2:20–22. - PubMed
-
- Stern RC, Borkat G, Hirschfeld SS, Boat TF, Matthews LW, Liebman J, Doershuk CF. Heart failure in cystic fibrosis. Treatment and prognosis of cor pulmonale with failure of the right side of the heart. Am J Dis Child. 1980;134:267–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL107577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 HL054705/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL76139-7/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL079650/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079650/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL035440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL054705/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL102235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122062/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL35440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL054705/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL102235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

