Regulation of IL-4 receptor signaling by STUB1 in lung inflammation
- PMID: 24251647
- PMCID: PMC3919125
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201305-0874OC
Regulation of IL-4 receptor signaling by STUB1 in lung inflammation
Abstract
Rationale: IL-4Rα, the common receptor component for IL-4 and IL-13, plays a critical role in IL-4- and IL-13-mediated signaling pathways that regulate airway inflammation and remodeling. However, the regulatory mechanisms underlying IL-4Rα turnover and its signal termination remain elusive.
Objectives: To evaluate the role of STUB1 (STIP1 homology and U-Box containing protein 1) in regulating IL-4R signaling in airway inflammation.
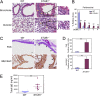
Methods: The roles of STUB1 in IL-4Rα degradation and its signaling were investigated by immunoblot, immunoprecipitation, and flow cytometry. The involvement of STUB1 in airway inflammation was determined in vivo by measuring lung inflammatory cells infiltration, mucus production, serum lgE levels, and alveolar macrophage M2 activation in STUB1(-/-) mice. STUB1 expression was evaluated in airway epithelium of patients with asthma and lung tissues of subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
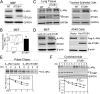
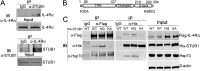
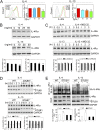
Measurements and main results: STUB1 interacted with IL-4Rα and targeted it for ubiquitination-mediated proteasomal degradation, terminating IL-4 or IL-13 signaling. STUB1 knockout cells showed increased levels of IL-4Rα and sustained STAT6 activation, whereas STUB1 overexpression reduced IL-4Rα levels. Mice deficient in STUB1 had spontaneous airway inflammation, alternative M2 activation of alveolar macrophage, and increased serum IgE. STUB1 levels were increased in airways of subjects with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, suggesting that up-regulation of STUB1 might be an important feedback mechanism to dampen IL-4R signaling in airway inflammation.
Conclusions: Our study identified a previously uncharacterized role for STUB1 in regulating IL-4R signaling, which might provide a new strategy for attenuating airway inflammation.
Figures



Comment in
-
IL-4Rα, a STUB-strate for proteasomal degradation: understanding the termination of cytokine signaling in asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Jan 1;189(1):4-6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201311-2083ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24381986 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mirel DB, Valdes AM, Lazzeroni LC, Reynolds RL, Erlich HA, Noble JA. Association of IL4R haplotypes with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:3336–3341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

