Kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside-7-O-rhamnoside is an endogenous flavonol inhibitor of polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis shoots
- PMID: 24251900
- PMCID: PMC4260840
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.12558
Kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside-7-O-rhamnoside is an endogenous flavonol inhibitor of polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis shoots
Abstract
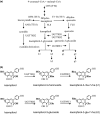
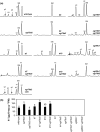
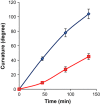
Polar auxin transport (PAT) plays key roles in the regulation of plant growth and development. Flavonoids have been implicated in the inhibition of PAT. However, the active flavonoid derivative(s) involved in this process in vivo has not yet been identified. Here, we provide evidence that a specific flavonol bis-glycoside is correlated with shorter plant stature and reduced PAT. Specific flavonoid-biosynthetic or flavonoid-glycosylating steps were genetically blocked in Arabidopsis thaliana. The differential flavonol patterns established were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and related to altered plant stature. PAT was monitored in stem segments using a radioactive [(3)H]-indole-3-acetic acid tracer. The flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase mutant ugt78d2 exhibited a dwarf stature in addition to its altered flavonol glycoside pattern. This was accompanied by reduced PAT in ugt78d2 shoots. The ugt78d2-dependent growth defects were flavonoid dependent, as they were rescued by genetic blocking of flavonoid biosynthesis. Phenotypic and metabolic analyses of a series of mutants defective at various steps of flavonoid formation narrowed down the potentially active moiety to kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside-7-O-rhamnoside. Moreover, the level of this compound was negatively correlated with basipetal auxin transport. These results indicate that kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside-7-O-rhamnoside acts as an endogenous PAT inhibitor in Arabidopsis shoots.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; flavonol biosynthesis; flavonol glycoside; flavonol glycosyltransferases; plant growth; polar auxin transport.
© 2013 The Authors New Phytologist © 2013 New Phytologist Trust.
Figures


References
-
- Abrahams S, Lee E, Walker AR, Tanner GJ, Larkin PJ, Ashton AR. The Arabidopsis TDS4 gene encodes leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX) and is essential for proanthocyanidin synthesis and vacuole development. Plant Journal. 2003;35:624–636. - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science. 2003;301:653–657. - PubMed
-
- Bailly A, Sovero V, Vincenzetti V, Santelia D, Bartnik D, Koenig BW, Mancuso S, Martinoia E, Geisler M. Modulation of P-glycoproteins by auxin transport inhibitors is mediated by interaction with immunophilins. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2008;283:21817–21826. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay A, Blakeslee JJ, Lee OR, Mravec J, Sauer M, Titapiwatanakun B, Makam SN, Bouchard R, Geisler M, Martinoia E, et al. Interactions of PIN and PGP auxin transport mechanisms. Biochemical Society Transactions. 2007;35:137–141. - PubMed
-
- Berleth T, Scarpella E, Prusinkiewicz P. Towards the systems biology of auxin-transport-mediated patterning. Trends in Plant Science. 2007;12:151–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

