Regulation of endogenous human gene expression by ligand-inducible TALE transcription factors
- PMID: 24251925
- PMCID: PMC4097969
- DOI: 10.1021/sb400114p
Regulation of endogenous human gene expression by ligand-inducible TALE transcription factors
Abstract
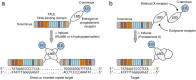
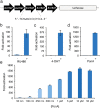
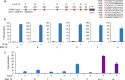
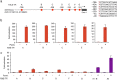
The construction of increasingly sophisticated synthetic biological circuits is dependent on the development of extensible tools capable of providing specific control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Here, we describe a new class of synthetic transcription factors that activate gene expression in response to extracellular chemical stimuli. These inducible activators consist of customizable transcription activator-like effector (TALE) proteins combined with steroid hormone receptor ligand-binding domains. We demonstrate that these ligand-responsive TALE transcription factors allow for tunable and conditional control of gene activation and can be used to regulate the expression of endogenous genes in human cells. Since TALEs can be designed to recognize any contiguous DNA sequence, the conditional gene regulatory system described herein will enable the design of advanced synthetic gene networks.
Keywords: TALE; gene regulation; inducible gene expression; steroid hormone receptor; transcription factor.
Figures
References
-
- Slusarczyk A. L.; Lin A.; Weiss R. (2012) Foundations for the design and implementation of synthetic genetic circuits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 406–420. - PubMed
-
- Folcher M.; Fussenegger M. (2012) Synthetic biology advancing clinical applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 16, 345–354. - PubMed
-
- Auslander S.; Fussenegger M. (2013) From gene switches to mammalian designer cells: present and future prospects. Trends Biotechnol. 31, 155–168. - PubMed
-
- Gardner T. S.; Cantor C. R.; Collins J. J. (2000) Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 403, 339–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

