Direct observation of multiple tautomers of oxythiamine and their recognition by the thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch
- PMID: 24252063
- PMCID: PMC3956446
- DOI: 10.1021/cb400581f
Direct observation of multiple tautomers of oxythiamine and their recognition by the thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch
Abstract
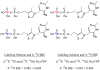
Structural diversification of canonical nucleic acid bases and nucleotide analogues by tautomerism has been proposed to be a powerful on/off switching mechanism allowing regulation of many biological processes mediated by RNA enzymes and aptamers. Despite the suspected biological importance of tautomerism, attempts to observe minor tautomeric forms in nucleic acid or hybrid nucleic acid-ligand complexes have met with challenges due to the lack of sensitive methods. Here, a combination of spectroscopic, biochemical, and computational tools probed tautomerism in the context of an RNA aptamer-ligand complex; studies involved a model ligand, oxythiamine pyrophosphate (OxyTPP), bound to the thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) riboswitch (an RNA aptamer) as well as its unbound nonphosphorylated form, oxythiamine (OxyT). OxyTPP, similarly to canonical heteroaromatic nucleic acid bases, has a pyrimidine ring that forms hydrogen bonding interactions with the riboswitch. Tautomerism was established using two-dimensional infrared (2D IR) spectroscopy, variable temperature FTIR and NMR spectroscopies, binding isotope effects (BIEs), and computational methods. All three possible tautomers of OxyT, including the minor enol tautomer, were directly identified, and their distributions were quantitated. In the bound form, BIE data suggested that OxyTPP existed as a 4'-keto tautomer that was likely protonated at the N1'-position. These results also provide a mechanistic framework for understanding the activation of riboswitch in response to deamination of the active form of vitamin B1 (or TPP). The combination of methods reported here revealing the fine details of tautomerism can be applied to other systems where the importance of tautomerism is suspected.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
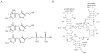





References
-
- Cochrane JC, Strobel SA. Catalytic Strategies of Self-Cleaving Ribozymes. Acc Chem Res. 2008;41:1027–1035. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Burke JM. Model for general acid-base catalysis by the hammerhead ribozyme: pH-activity relationships of G8 and G12 variants at the putative active site. Biochemistry. 2005;44:7864–7870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

