The prion hypothesis in Parkinson's disease: Braak to the future
- PMID: 24252164
- PMCID: PMC3776210
- DOI: 10.1186/2051-5960-1-2
The prion hypothesis in Parkinson's disease: Braak to the future
Abstract
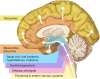
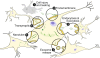
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder typified by the presence of intraneuronal inclusions containing aggregated alpha synuclein (αsyn). The progression of parkinsonian pathology and clinical phenotype has been broadly demonstrated to follow a specific pattern, most notably described by Braak and colleagues. In more recent times it has been hypothesized that αsyn itself may be a critical factor in mediating transmission of disease pathology from one brain area to another. Here we investigate the growing body of evidence demonstrating the ability of αsyn to spread transcellularly and induce pathological aggregation affecting neurons by permissive templating and provide a critical analysis of some irregularities in the hypothesis that the progression of PD pathology may be mediated by such a prion-like process. Finally we discuss some key questions that remain unanswered which are vital to determining the potential contribution of a prion-like process to the pathogenesis of PD.
Figures
References
-
- Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, Akiyama H, Caviness JN, Shill HA, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG. Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119:689–702. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0664-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

