Dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathway in hematological malignancies and JAK inhibitors for clinical application
- PMID: 24252238
- PMCID: PMC3776247
- DOI: 10.1186/2050-7771-1-5
Dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathway in hematological malignancies and JAK inhibitors for clinical application
Abstract
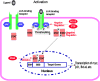
JAK-STAT (Janus associated kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway plays a critical role in transduction of extracellular signals from cytokines and growth factors involved in hematopoiesis, immune regulation, fertility, lactation, growth and embryogenesis. JAK family contains four cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases, JAK1-3 and Tyk2. Seven STAT proteins have been identified in human cells, STAT1-6, including STAT5a and STAT5b. Negative regulators of JAK-STAT pathways include tyrosine phosphatases (SHP1 and 2, CD45), protein inhibitors of activated STATs (PIAS), suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins, and cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein (CIS). Dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathway have been found to be key events in a variety of hematological malignancies. JAK inhibitors are among the first successful agents reaching clinical application. Ruxolitinib (Jakafi), a non-selective inhibitor of JAK1 & 2, has been approved by FDA for patients with intermediate to high risk primary or secondary myelofibrosis. This review will also summarize early data on selective JAK inhibitors, including SAR302503 (TG101348), lestaurtinib (CEP701), CYT387, SB1518 (pacritinib), LY2784544, XL019, BMS-911543, NS-018, and AZD1480.
Figures
References
-
- Friedrich K, Kammer W, Erhardt I, Brandlein S, Sebald W, Moriggl R. Activation of STAT5 by IL-4 relies on Janus kinase function but not on receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, and can contribute to both cell proliferation and gene regulation. Int Immunol. 1999;11(8):1283–1294. doi: 10.1093/intimm/11.8.1283. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

