Proteomic analysis reveals heat shock protein 70 has a key role in polycythemia Vera
- PMID: 24252366
- PMCID: PMC4225507
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-142
Proteomic analysis reveals heat shock protein 70 has a key role in polycythemia Vera
Abstract
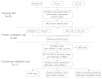
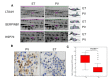
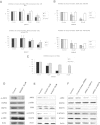
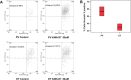
JAK-STAT signaling through the JAK2V617F mutation is central to the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN). However, other events could precede the JAK2 mutation. The aim of this study is to analyze the phenotypic divergence between polycytemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocytemia (ET) to find novel therapeutics targets by a proteomic and functional approach to identify alternative routes to JAK2 activation. Through 2D-DIGE and mass spectrometry of granulocyte protein from 20 MPN samples, showed differential expression of HSP70 in PV and ET besides other 60 proteins. Immunohistochemistry of 46 MPN bone marrow samples confirmed HSP70 expression. The median of positive granulocytes was 80% in PV (SD 35%) vs. 23% in ET (SD 34.25%). In an ex vivo model KNK437 was used as an inhibition model assay of HSP70, showed dose-dependent inhibition of cell growth and burst formation unit erythroid (BFU-E) in PV and ET, increased apoptosis in the erythroid lineage, and decreased pJAK2 signaling, as well as a specific siRNA for HSP70. These data suggest a key role for HSP70 in proliferation and survival of the erythroid lineage in PV, and may represent a potential therapeutic target in MPN, especially in PV.
Figures
References
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365(9464):1054–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

