Regulation of the expression level of transcription factor XylS reveals new functional insight into its induction mechanism at the Pm promoter
- PMID: 24252441
- PMCID: PMC4225500
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-262
Regulation of the expression level of transcription factor XylS reveals new functional insight into its induction mechanism at the Pm promoter
Abstract
Background: XylS is the positive regulator of the inducible Pm promoter, originating from Pseudomonas putida, where the system controls a biochemical pathway involved in degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons, which also act as inducers. The XylS/Pm positive regulator/promoter system is used for recombinant gene expression and the output from Pm is known to be sensitive to the intracellular XylS concentration.
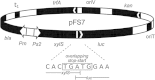
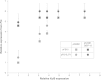
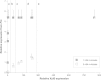
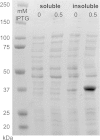
Results: By constructing a synthetic operon consisting of xylS and luc, the gene encoding luciferase, relative XylS expression levels could be monitored indirectly at physiological concentrations. Expression of XylS from inducible promoters allowed control over a more than 800-fold range, however, the corresponding output from Pm covered only an about five-fold range. The maximum output from Pm could not be increased by introducing more copies of the promoter in the cells. Interestingly, a previously reported XylS variant (StEP-13), known to strongly stimulate expression from Pm, caused the same maximum activity from Pm as wild-type XylS at high XylS expression levels. Under uninduced conditions expression from Pm also increased as a function of XylS expression levels, and at very high concentrations the maximum activity from Pm was the same as in the presence of inducer.
Conclusion: According to our proposed model, which is in agreement with current knowledge, the regulator, XylS, can exist in three states: monomers, dimers, and aggregates. Only the dimers are active and able to induce expression from Pm. Their maximum intracellular concentration and the corresponding output from Pm are limited by the concentration-dependent conversion into inactive aggregates. Maximization of the induction ratio at Pm can be obtained by expression of XylS at the level where aggregation occurs, which might be exploited for recombinant gene expression. The results described here also indicate that there might exist variants of XylS which can exist at higher active dimer concentrations and thus lead to increased expression levels from Pm.
Figures


References
-
- Mergulhão FJM, Monteiro GA, Cabral JMS, Taipa MA. Design of bacterial vector systems for the production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;14:1–14.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

