Eyeballing cholesterol efflux and macrophage function in disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 24252662
- PMCID: PMC3943676
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2013.10.007
Eyeballing cholesterol efflux and macrophage function in disease pathogenesis
Abstract
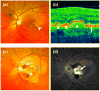
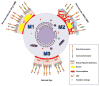
Disorders of lipid metabolism are strongly associated with cardiovascular disease. Recently, there has been significant focus on how tissues process lipid deposits. Impaired cholesterol efflux has been shown to be crucial in mediating lipid deposition in atherosclerosis. The inability of macrophages to effectively efflux cholesterol from tissues initiates inflammation, plaque neovascularization, and subsequent rupture. Recent studies suggest that inability to effectively efflux cholesterol from tissues may have global implications far beyond atherosclerosis, extending to the pathophysiology of unrelated diseases. We examine the unifying mechanisms by which impaired cholesterol efflux facilitates tissue-specific inflammation and disease progression in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a blinding eye disease, and in atherosclerosis, a disease associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity.
Keywords: AMD; atherosclerosis; cholesterol efflux; lipids; macrophage.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman DS, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States. Archives of ophthalmology. 2004;122:564–572. - PubMed
-
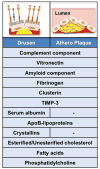
- Hageman GS, et al. An integrated hypothesis that considers drusen as biomarkers of immune-mediated processes at the RPE-Bruch’s membrane interface in aging and age-related macular degeneration. Progress in retinal and eye research. 2001;20:705–732. - PubMed
-
- Zipfel PF, et al. The role of complement in AMD. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2010;703:9–24. - PubMed
-
- Cherepanoff S, et al. Bruch’s membrane and choroidal macrophages in early and advanced age-related macular degeneration. The British journal of ophthalmology. 2010;94:918–925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

