The onset of C. elegans dosage compensation is linked to the loss of developmental plasticity
- PMID: 24252776
- PMCID: PMC3891041
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.11.001
The onset of C. elegans dosage compensation is linked to the loss of developmental plasticity
Abstract
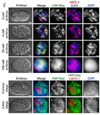
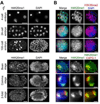
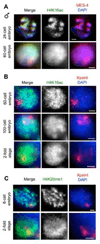
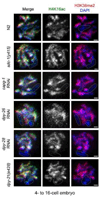
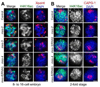
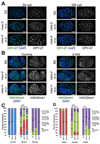
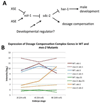
Dosage compensation (DC) equalizes X-linked gene expression between sexes. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the dosage compensation complex (DCC) localizes to both X chromosomes in hermaphrodites and downregulates gene expression 2-fold. The DCC first localizes to hermaphrodite X chromosomes at the 30-cell stage, coincident with a developmental transition from plasticity to differentiation. To test whether DC onset is linked to loss of developmental plasticity, we established a timeline for the accumulation of DC-mediated chromatin features on X (depletion of histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation (H4K16ac) and enrichment of H4K20 monomethylation (H4K20me1)) in both wild type and developmentally delayed embryos. Surprisingly, we found that H4K16ac is depleted from the X even before the 30-cell stage in a DCC-independent manner. This depletion requires the activities of MES-2, MES-3, and MES-6 (a complex similar to the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2), and MES-4. By contrast, H4K20me1 becomes enriched on X chromosomes several cell cycles after DCC localization to the X, suggesting that it is a late mark in DC. MES-2 also promotes differentiation, and mes-2 mutant embryos exhibit prolonged developmental plasticity. Consistent with the hypothesis that the onset of DC is linked to differentiation, DCC localization and H4K20me1 accumulation on the X chromosomes are delayed in mes mutant hermaphrodite embryos. Furthermore, the onset of hermaphrodite-specific transcription of sdc-2 (which triggers DC) is delayed in mes-2 mutants. We propose that as embryonic blastomeres lose their developmental plasticity, hermaphrodite X chromosomes transition from a MES protein-regulated state to DCC-mediated repression.
Keywords: Chromatin; Dosage compensation; Epigenetics; Pluripotency.
© 2013 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Akhtar A, Becker PB. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol Cell. 2000;5:367–375. - PubMed
-
- Barakat TS, Gribnau J. X chromosome inactivation in the cycle of life. Development. 2012;139:2085–2089. - PubMed
-
- Baugh LR, Hill AA, Slonim DK, Brown EL, Hunter CP. Composition and dynamics of the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryonic transcriptome. Development. 2003;130:889–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

