Multiple tendon xanthomas in patient with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: sonographic and MRI findings
- PMID: 24252837
- PMCID: PMC3841438
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200755
Multiple tendon xanthomas in patient with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: sonographic and MRI findings
Abstract
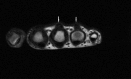
Tendon xanthomas are a component of familial hypercholesterolaemia, which is a hereditary disease and characterised by elevated low-density lipo protein cholesterol plasma levels and premature coronary artery disease. Tendon xanthomas are diagnostic for heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (HFH) and they mostly occur in Achilles tendon. Sonography and MRI are superior to clinical assessment and are useful in detecting tendon xanthomas. In this report, we present ultrasonographic and MRI findings of multiple tendon xanthomas in a case of HFH.
Figures


References
-
- Bureau NJ, Roederer G. Sonography of Achilles tendon xanthomas in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. AJR 1998;2013:745–9 - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto A, Kamiya T, Yamamura T, et al. Clinical features of familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis 1989;2013:166–74 - PubMed
-
- Bude RO, Adler AS, Bassett DR. Diagnosis of Achilles tendon xanthoma in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: MR vs sonography. AJR 1994;2013:913–17 - PubMed
-
- Smithard A, Lamyman MJ, McCarthy CL, et al. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis presenting with bilateral Achilles tendon xanthomata. Skeletal Radiol 2007;2013:171–5 - PubMed
-
- Gattereau A, Davignon J, Levesque HP. Roentgenological evaluation of Achilles-tendon xanthomatosis. Lancet 1971;2013:705–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
