Proteomics of cancer cell lines resistant to microtubule-stabilizing agents
- PMID: 24252851
- PMCID: PMC3947109
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0471
Proteomics of cancer cell lines resistant to microtubule-stabilizing agents
Abstract
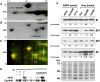
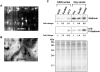
Despite the clinical success of microtubule-interacting agents (MIA), a significant challenge for oncologists is the inability to predict the response of individual patients with cancer to these drugs. In the present study, six cell lines were compared by 2D DIGE proteomics to investigate cellular resistance to the class of MIAs known as microtubule-stabilizing agents (MSA). The human lung cancer cell line A549 was compared with two drug-resistant daughter cell lines, a taxol-resistant cell line (AT12) and an epothilone B (EpoB)-resistant cell line (EpoB40). The ovarian cancer cell line Hey was compared with two drug-resistant daughter cell lines, an EpoB-resistant cell line (EpoB8) and an ixabepilone-resistant cell line (Ixab80). All 2D DIGE results were validated by Western blot analyses. A variety of cytoskeletal and cytoskeleton-associated proteins were differentially expressed in drug-resistant cells. Differential abundance of 14-3-3σ, galectin-1 and phosphorylation of stathmin are worthy of further studies as candidate predictive biomarkers for MSAs. This is especially true for galectin-1, a β-galactose-binding lectin that mediates tumor invasion and metastasis. Galectin-1 was greatly increased in EpoB- and ixabepilone-resistant cells and its suppression caused an increase in drug sensitivity in both drug-sensitive and -resistant Hey cells. Furthermore, the growth medium from resistant Hey cells contained higher levels of galectin-1, suggesting that galectin-1 could play a role in resistance to MSAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kavallaris M. Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:194–204. - PubMed
-
- Cortes J, Montero AJ, Gluck S. Eribulin mesylate, a novel microtubule inhibitor in the treatment of breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012;38:143–51. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla KN. Microtubule-targeted anticancer agents and apoptosis. Oncogene. 2003;22:9075–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

