Primary total hip arthroplasty: health related quality of life outcomes
- PMID: 24252971
- PMCID: PMC3936080
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-013-2142-8
Primary total hip arthroplasty: health related quality of life outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: The health related quality of life (HRQoL) outcomes of total hip arthroplasty (THA) present a pertinent and clinically important problem in modern orthopaedics. Our goal was to report and compare the health-related outcomes after THA in respect to type of fixation in patients with hip osteoarthritis (H-OA) one year after operation.
Methods: A total of 145 patients with H-OA who received THA were evaluated. Uncemented and cemented subjects were evaluated using generic measures, i.e. the EQ-5D questionnaire, and the disease-specific measures designed by the authors, i.e. the Total Hip Arthroplasty Questionnaire (THAQ). Obtained data was statistically processed at the level of pain, functionality and general health perception. Patient-reported outcomes were measured differences between pre-operative measures and those at one-year follow-up visit.
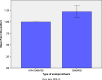
Results: Significant improvement in health outcomes was reached in both groups regardless of the type of fixation (p < 0.001). Uncemented fixation exhibited better results for EQ-5DINDEX, pain (p = 0.004) and self-care on EQ-5D (p = 0.043), as well as increased magnitude of change for functionality on THAQ (p = 0.002). However, additional analysis of the subset did not reveal a significant difference between cemented vs. uncemented groups with regard to function on THAQ, but the significant difference on self-care and pain dimensions of EQ-5D remained.
Conclusions: Uncemented endoprosthesis generally achieved better short-term outcomes in some dimensions. However, painless mobility has been restored in most of the patients, regardless of the fixation type. Both methods reached good clinical outcomes in their respective domains; therefore, we would emphasise prevention of osteoarthritis and the quality of care as the more important predictors of good clinical outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Ethgen O, Bruyere O, Richy F, Dardennes C, Reginster JY. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(5):963–974. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical