Anti-inflammatory effects of the Chinese herbal formula FAHF-2 in experimental and human IBD
- PMID: 24252977
- PMCID: PMC4631125
- DOI: 10.1097/01.MIB.0000436467.37566.48
Anti-inflammatory effects of the Chinese herbal formula FAHF-2 in experimental and human IBD
Abstract
Background: Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory disease with increasing incidence in children. Current medications have potentially serious side effects, hence increasing interest in alternative therapies. We previously developed an herbal formula, FAHF-2, based on a classical traditional Chinese herbal formula Wu Mei Wan that has long been used in China to treat colitis. We investigated FAHF-2's potential anti-inflammatory effects.
Methods: FAHF-2 efficacy was tested in vivo in the CD45RbRAG1 transfer colitis model. Weight loss, colonic histology, and cytokine production from mesenteric lymph nodes were assessed. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and colonic biopsies were obtained from children newly diagnosed with CD and controls and cultured with or without FAHF-2. Cytokine levels were measured by multiplex immunoassay. The effect of FAHF-2 on TNF-α-producing cells was determined by flow cytometry. NF-κB signaling was investigated in human lamina propria mononuclear cells upon FAHF-2 treatment by In-Cell Western.
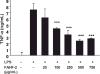
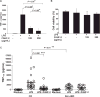
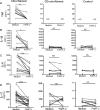
Results: FAHF-2-treated mice had decreased weight loss, improved histology, and reduced TNF-α, IL-17, IL-6, and IFN-γ production. In vitro treated PBMCs produced less TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-12. FAHF-2 reduced the TNF-α-producing monocytes and T cells. Inflamed CD biopsies produced less TNF-α, IL-17, IL-6, and IL-1β. These effects are because of decreased NF-κB activation.
Conclusions: FAHF-2 inhibited both adaptive and innate immune proinflammatory cytokine responses in PBMCs and inflamed CD mucosa due in part to blockage of NF-κB activation. FAHF-2 was effective in halting progression of colitis in a murine model. This study shows that FAHF-2 has potential as a novel treatment of CD.
Conflict of interest statement
X.-M. Li is a consultant for the FAI and has shares of US Patent PCT/US 05/08600 on FAHF-2 and Herbal Springs, LLC. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, Casparie M, Taminiau JA, et al. The incidence of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in the Netherlands: 1999–2001. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;38:302–307. - PubMed
-
- Benchimol EI, Fortinsky KJ, Gozdyra P, et al. Epidemiology of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of international trends. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:423–439. - PubMed
-
- Benchimol EI, Guttmann A, Griffiths AM, et al. Increasing incidence of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Ontario, Canada: evidence from health administrative data. Gut. 2009;58:1490–1497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

