Targeting C-myc G-quadruplex: dual recognition by aminosugar-bisbenzimidazoles with varying linker lengths
- PMID: 24252993
- PMCID: PMC6270413
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules181114228
Targeting C-myc G-quadruplex: dual recognition by aminosugar-bisbenzimidazoles with varying linker lengths
Abstract
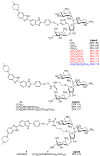
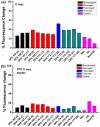
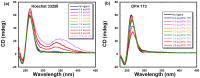
G-quadruplexes are therapeutically important biological targets. In this report, we present biophysical studies of neomycin-Hoechst 33258 conjugates binding to a G-quadruplex derived from the C-myc promoter sequence. Our studies indicate that conjugation of neomycin to a G-quadruplex binder, Hoechst 33258, enhances its binding. The enhancement in G-quadruplex binding of these conjugates varies with the length and composition of the linkers joining the neomycin and Hoechst 33258 units.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

