Proteinase-activated receptor-2 transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor and transforming growth factor-β receptor signaling pathways contributes to renal fibrosis
- PMID: 24253040
- PMCID: PMC3873584
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492793
Proteinase-activated receptor-2 transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor and transforming growth factor-β receptor signaling pathways contributes to renal fibrosis
Abstract
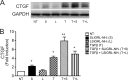
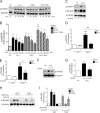
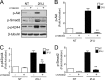
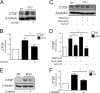
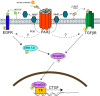
Chronic kidney diseases cause significant morbidity and mortality in the population. During renal injury, kidney-localized proteinases can signal by cleaving and activating proteinase-activated receptor-2 (PAR2), a G-protein-coupled receptor involved in inflammation and fibrosis that is highly expressed in renal tubular cells. Following unilateral ureteric obstruction, PAR2-deficient mice displayed reduced renal tubular injury, fibrosis, collagen synthesis, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and α-smooth muscle actin gene expression at 7 days, compared with wild-type controls. In human proximal tubular epithelial cells in vitro, PAR2 stimulation with PAR2-activating peptide (PAR2-AP) alone significantly up-regulated the expression of CTGF, a potent profibrotic cytokine. The induction of CTGF by PAR2-AP was synergistically increased when combined with transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). Consistent with these findings, treating human proximal tubular epithelial cells with PAR2-AP induced Smad2/3 phosphorylation in the canonical TGF-β signaling pathway. The Smad2 phosphorylation and CTGF induction required signaling via both the TGFβ-receptor and EGF receptor suggesting that PAR2 utilizes transactivation mechanisms to initiate fibrogenic signaling. Taken together, our data support the hypothesis that PAR2 synergizes with the TGFβ signaling pathway to contribute to renal injury and fibrosis.
Keywords: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR); Fibrosis; Kidney; PAR2; Receptors; Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFβ).
Figures







References
-
- Ali T., Khan I., Simpson W., Prescott G., Townend J., Smith W., Macleod A. (2007) Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury. A comprehensive population-based study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 1292–1298 - PubMed
-
- Eddy A. A. (2000) Molecular basis of renal fibrosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 15, 290–301 - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran R., Noorbakhsh F., Defea K., Hollenberg M. D. (2012) Targeting proteinase-activated receptors. Therapeutic potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 69–86 - PubMed
-
- Rothmeier A. S., Ruf W. (2012) Protease-activated receptor 2 signaling in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 34, 133–149 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

