Longitudinal effects of a decade of aging on carotid artery stiffness: the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 24253542
- PMCID: PMC3888489
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.002649
Longitudinal effects of a decade of aging on carotid artery stiffness: the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Arterial stiffening is associated with hypertension, stroke, and cognitive decline; however, the effects of aging and cardiovascular disease risk factors on carotid artery stiffening have not been assessed prospectively in a large multiethnic longitudinal study.
Methods: Distensibility coefficient and the Young's elastic modulus (YEM) of the right common carotid artery were calculated at baseline and after a mean of 9.4 (standard deviation [SD], 0.5) years in 2650 participants. Effects of age and cardiovascular disease risk factors were evaluated by multivariable mixed regression and ANCOVA models.
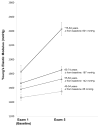
Results: At baseline, participants were 59.9 (SD, 9.4) years old (53% women; 25% black, 22% Hispanic, 14% Chinese). YEM increased from 1581 (SD, 927) to 1749 (SD, 1306) mm Hg (P<0.0001), and distensibility coefficient decreased from 3.1 (SD, 1.3) to 2.7 (SD, 1.1)×10(-3) mm Hg(-1) (P<0.001), indicating progressive arterial stiffening. YEM increased more among participants who were aged>75 years old at baseline (P<0.0001). In multivariable analyses, older age and less education independently predicted worsening YEM and distensibility coefficient. Stopping antihypertensive medication during the study period predicted more severe worsening of YEM (β=360.2 mm Hg; P=0.008). Starting antihypertensive medication after examination 1 was predictive of improvements in distensibility coefficient (β=1.1×10(-4) mm Hg(-1); P=0.024).
Conclusions: Arterial stiffening accelerates with advanced age. Older individuals experience greater increases in YEM than do younger adults, even after considering the effects of traditional risk factors. Treating hypertension may slow the progressive decline in carotid artery distensibility observed with aging and improve cerebrovascular health.
Keywords: aging; carotid arteries; elasticity; hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Sharrett AR, Ding J, Criqui MH, Saad MF, Liu K, Polak JF, et al. Smoking, diabetes, and blood cholesterol differ in their associations with subclinical atherosclerosis: the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Atherosclerosis. 2006;186:441–447. - PubMed
-
- Safar ME. Systolic hypertension in the elderly: arterial wall mechanical properties and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. J Hypertens. 2005;23:673–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RD831697/RD/ORD VA/United States
- T32 HL007936/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HC95159-HC95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL07936/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD010569/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES015459/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32ES015459/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 ES015915/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL07936/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES015915/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL094760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 ES013195/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases