The mechanism by which MEK/ERK regulates JNK and p38 activity in polyamine depleted IEC-6 cells during apoptosis
- PMID: 24253595
- PMCID: PMC4061750
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-013-0944-1
The mechanism by which MEK/ERK regulates JNK and p38 activity in polyamine depleted IEC-6 cells during apoptosis
Abstract
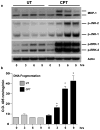
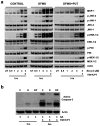
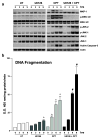
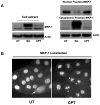
Polyamine-depletion inhibited apoptosis by activating ERK1/2, while, preventing JNK1/2 activation. MKP-1 knockdown by SiRNA increased ERK1/2, JNK1/2, and p38 phosphorylation and apoptosis. Therefore, we predicted that polyamines might regulate MKP1 via MEK/ERK and thereby apoptosis. We examined the role of MEK/ERK in the regulation of MKP1 and JNK, and p38 activities and apoptosis. Inhibition of MKP-1 activity with a pharmacological inhibitor, sanguinarine (SA), increased JNK1/2, p38, and ERK1/2 activities without causing apoptosis. However, pre-activation of these kinases by SA significantly increased camptothecin (CPT)-induced apoptosis suggesting different roles for MAPKs during survival and apoptosis. Inhibition of MEK1 activity prevented the expression of MKP-1 protein and augmented CPT-induced apoptosis, which correlated with increased activities of JNK1/2, caspases, and DNA fragmentation. Polyamine depleted cells had higher levels of MKP-1 protein and decreased JNK1/2 activity and apoptosis. Inhibition of MEK1 prevented MKP-1 expression and increased JNK1/2 and apoptosis. Phospho-JNK1/2, phospho-ERK2, MKP-1, and the catalytic subunit of PP2Ac formed a complex in response to TNF/CPT. Inactivation of PP2Ac had no effect on the association of MKP-1 and JNK1. However, inhibition of MKP-1 activity decreased the formation of the MKP-1, PP2Ac and JNK complex. Following inhibition by SA, MKP-1 localized in the cytoplasm, while basal and CPT-induced MKP-1 remained in the nuclear fraction. These results suggest that nuclear MKP-1 translocates to the cytoplasm, binds phosphorylated JNK and p38 resulting in dephosphorylation and decreased activity. Thus, MEK/ERK activity controls the levels of MKP-1 and, thereby, regulates JNK activity in polyamine-depleted cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Regulation of JNK activity in the apoptotic response of intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):G761-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00405.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21350193 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in polyamine-depleted IEC-6 cells is mediated through the activation of ERK1/2.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004 Mar;286(3):G479-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00342.2003. Epub 2003 Oct 16. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14563673
-
The decrease in JNK- and p38-MAP kinase activity is accompanied by the enhancement of PP2A phosphate level in the brain of prenatally stressed rats.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;61(2):207-15. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20436222
-
Acetylation of MKP-1 and the control of inflammation.Sci Signal. 2008 Oct 14;1(41):pe44. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.141pe44. Sci Signal. 2008. PMID: 18922786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protecting the stress response, guarding the MKP-1 mRNA.Cell Cycle. 2008 Sep 1;7(17):2640-2. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.17.6534. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18728392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling through the S1P-S1PR Axis in the Gut, the Immune and the Central Nervous System in Multiple Sclerosis: Implication for Pathogenesis and Treatment.Cells. 2021 Nov 18;10(11):3217. doi: 10.3390/cells10113217. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibitors and T-Cell-Dependent Immunotherapy in Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Jan 7;13(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ph13010009. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DGCR5 Promotes Gallbladder Cancer by Sponging MiR-3619-5p via MEK/ERK1/2 and JNK/p38 MAPK Pathways.J Cancer. 2020 Jul 11;11(18):5466-5477. doi: 10.7150/jca.46351. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32742494 Free PMC article.
-
ERK2 and JNK1 contribute to TNF-α-induced IL-8 expression in synovial fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 14;12(8):e0182923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182923. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28806729 Free PMC article.
-
Nonmineralized and Mineralized Collagen Scaffolds Induce Differential Osteogenic Signaling Pathways in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 Dec;6(23):10.1002/adhm.201700641. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700641. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. PMID: 28945007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tabor CW, Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Baylin SB, Luk GD. Polyamines and intestinal growth: absolute requirement for ODC activity in adaptation during lactation. Am J Physiol. 1984;247:G553–G557. - PubMed
-
- Luk GD, Baylin SB. Polyamines and intestinal growth-increased polyamine biosynthesis after jejunectomy. Am J Physiol. 1983;245:G656–G660. - PubMed
-
- Wang JY, Johnson LR. Luminal polyamines stimulate repair of gastric mucosal stress ulcers. Am J Physiol. 1990;259:G584–G592. - PubMed
-
- Ray RM, McCormack SA, Johnson LR. Polyamine depletion arrests growth of IEC-6 and Caco-2 cells by different mechanisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281(1):G37–G43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

