Pthlh, a promising cancer modifier gene in rat tongue carcinogenesis
- PMID: 24253735
- PMCID: PMC3868494
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2013.2859
Pthlh, a promising cancer modifier gene in rat tongue carcinogenesis
Abstract
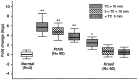
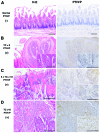
Susceptibly to the induction of rat tongue cancer (TC) by oral 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4NQO) exposure is a polygenic trait. Among several quantitative trait loci identified by crosses between TC-susceptible Dark Agouti (DA) rats and TC-resistant Wistar-Furth (WF) rats, we focused on tongue cancer susceptibility locus (Tcas3) of chromosome 4. We examined tongue carcinogenesis in the reciprocal congenic strains DA.WF-Tcas3 and WF.DA-Tcas3 and in their parental strains. The Tcas3DA allele, and not the Tcas3WF allele, significantly favored tumor latency, incidence and TC number/size. In genomic DNA of TCs induced in (DA x WF) F1 rats, the resistant Tcas3WF allele was frequently and selectively lost, particularly in larger tumors. Thus, we searched the possible candidate genes in the Tcas3 region using microarray analysis of TCs in F1 rats and revealed significant upregulation of 2 cancer-related genes, parathyroid hormone-like hormone (Pthlh) and Kras2. The relevance of the WF allele of Pthlh as a cancer modifier was indicated by 3 single nucleotide polymorphisms specific to this strain. In contrast, no consistent strain-specific variations were found in Kras2. Moreover, the plasma Ca2+ level was consistently higher in DA rats when compared to the level in WF rats bearing TCs; moreover, the Pthlh-mRNA expression level was >30-fold higher in TCs when compared to this level in the normal tongue mucosa. Immunostaining experiments showed strong PTHrP protein expression in TCs of DA rats, and the signal was intensified in larger TCs. Kras2 was also upregulated in TCs, but to a lesser degree than PTHrP. Thus, Pthlh is a promising candidate modifier gene in the development and progression of rat TCs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A speed congenic rat strain bearing the tongue cancer susceptibility locus Tscc1 from Dark-Agouti rats.Cancer Lett. 2006 Jan 18;231(2):185-91. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.01.043. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 15876484
-
Genetic predisposition to 4NQO-induced tongue carcinogenesis in the rat.Med Princ Pract. 2005 Sep-Oct;14(5):297-305. doi: 10.1159/000086926. Med Princ Pract. 2005. PMID: 16103694
-
Quantitative trait loci affecting 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced tongue carcinogenesis in the rat.Cancer Res. 1998 Apr 15;58(8):1660-4. Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9563479
-
Genetic controls of susceptibility and resistance to 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced tongue carcinomas in rats.Jpn J Cancer Res. 1996 Nov;87(11):1097-101. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1996.tb03116.x. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 9045935 Free PMC article.
-
Host genes controlling the susceptibility and resistance to squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in a rat model.Pathol Int. 2000 May;50(5):353-62. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2000.01058.x. Pathol Int. 2000. PMID: 10849324 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel cytological model for the identification of early oral cancer diagnostic markers: The carcinoma sequence model.Oncol Lett. 2022 Mar;23(3):76. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13196. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35111245 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed genes in the temporomandibular joint internal derangement.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2023 Aug;9(4):641-652. doi: 10.1002/cre2.768. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2023. PMID: 37555363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanuma J, Shisa H, Hiai H, et al. Quantitative trait loci affecting 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced tongue carcinogenesis in the rat. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1660–1664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

