Retinoid uptake, processing, and secretion in human iPS-RPE support the visual cycle
- PMID: 24255038
- PMCID: PMC4588713
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.13-11740
Retinoid uptake, processing, and secretion in human iPS-RPE support the visual cycle
Abstract
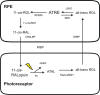
Purpose: Retinal pigmented epithelium derived from human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells (iPS-RPE) may be a source of cells for transplantation. For this reason, it is essential to determine the functional competence of iPS-RPE. One key role of the RPE is uptake and processing of retinoids via the visual cycle. The purpose of this study is to investigate the expression of visual cycle proteins and the functional ability of the visual cycle in iPS-RPE.
Methods: iPS-RPE was derived from human iPS cells. Immunocytochemistry, RT-PCR, and Western blot analysis were used to detect expression of RPE genes lecithin-retinol acyl transferase (LRAT), RPE65, cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein (CRALBP), and pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). All-trans retinol was delivered to cultured cells or whole cell homogenate to assess the ability of the iPS-RPE to process retinoids.
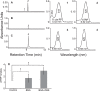
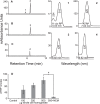
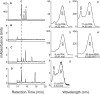
Results: Cultured iPS-RPE expresses visual cycle genes LRAT, CRALBP, and RPE65. After incubation with all-trans retinol, iPS-RPE synthesized up to 2942 ± 551 pmol/mg protein all-trans retinyl esters. Inhibition of LRAT with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) prevented retinyl ester synthesis. Significantly, after incubation with all-trans retinol, iPS-RPE released 188 ± 88 pmol/mg protein 11-cis retinaldehyde into the culture media.
Conclusions: iPS-RPE develops classic RPE characteristics and maintains expression of visual cycle proteins. The results of this study confirm that iPS-RPE possesses the machinery to process retinoids for support of visual pigment regeneration. Inhibition of all-trans retinyl ester accumulation by NEM confirms LRAT is active in iPS-RPE. Finally, the detection of 11-cis retinaldehyde in the culture medium demonstrates the cells' ability to process retinoids through the visual cycle. This study demonstrates expression of key visual cycle machinery and complete visual cycle activity in iPS-RPE.
Keywords: induced-pluripotent stem cell; retinal pigment epithelium; visual cycle.
Figures


References
-
- La Cour M, Tezel T. The retinal pigment epithelium. Adv Organ Biol. 2006; 10: 253–273.
-
- Dowling JE. Chemistry of visual adaptation in the rat. Nature. 1960; 188: 114–118. - PubMed
-
- McBee JK, Palczewski K, Baehr W, Pepperberg DR. Confronting complexity: the interlink of phototransduction and retinoid metabolism in the vertebrate retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001; 20: 469–529. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman WF. The distribution and proportions of vitamin A compounds during the visual cycle in the rat. Vision Res. 1974; 14: 795–802. - PubMed
-
- Saari JC, Bredberg DL. Lecithin: retinol acyltransferase in retinal pigment epithelial microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1989; 264: 8636–8640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

