Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitor E7080 and eNOS inhibitor L-NIO on colorectal cancer alone and in combination
- PMID: 24255582
- PMCID: PMC3828440
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.10.10
Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitor E7080 and eNOS inhibitor L-NIO on colorectal cancer alone and in combination
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of E7080 and N (5)-(1-iminoethyl)-L-ornithine dihydrochloride (L-NIO) on colorectal cancer alone and in combination.
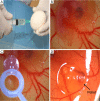
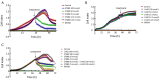
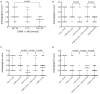
Methods: HT29 colorectal cancer cell line from Sap Institute was used. Real-time cell analysis (xCELLigence system) was performed to determine the effects of E7080 and L-NIO on colorectal cell proliferation. While apoptosis was determined with Annexin V staining, and the effect of agents on angiogenesis was determined with chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model.
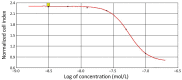
Results: We found that E7080 has a strong antiproliferative effect with an half maximum inhibition of concentration (IC50) value of 5.60×10(-8) mol/L. Also it has been observed that E7080 showed antiangiogenic and apoptotic effects on HT29 colorectal cancer cells. Antiangiogenic scores of E7080 were 1.2, 1.0 and 0.6 for 100, 10 and 1 nmol/L E7080 concentrations, respectively. Furthermore, apoptosis has been detected in 71% of HT29 colorectal cancer cells after administration of 100 nmol/L E7080 which may indicate strong apoptotic effect. Meanwhile administration of L-NIO alone did not show any effect, but the combination of E7080 with L-NIO increased the antiproliferative, antiangiogenic and apoptotic effects of E7080.
Conclusions: Results of this study indicate that E7080 may be a good choice in treatment of colorectal tumors. Furthermore the increased effects of E7080 when combined with L-NIO raise the possibility to use a lower dose of E7080 and therefore avoid/minimize the side effects observed with E7080.
Keywords: E7080; N5-(1-iminoethyl)-L-ornithine dihydrochloride (L-NIO); colorectal cancer; tyrosine kinase (TK); xCELLigence system.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010;127:2893-917 - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010;60:277-300 - PubMed
-
- Nasti G, Ottaiano A, Berretta M, et al. Pre-operative chemotherapy for colorectal cancer liver metastases: an update of recent clinical trials. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2010;66:209-18 - PubMed
-
- Köhne CH, Wils J, Lorenz M, et al. Randomized phase III study of high-dose fluorouracil given as a weekly 24-hour infusion with or without leucovorin versus bolus fluorouracil plus leucovorin in advanced colorectal cancer: European organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer Gastrointestinal Group Study 40952. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:3721-8 - PubMed
-
- Comella P, Casaretti R, Sandomenico C, et al. Capecitabine, alone or in combination, in the management of patients with colorectal cancer: a review of the evidence. Drugs 2008;68:949-61 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
