Apoptosis of bladder transitional cell carcinoma T24 cells induced by adenovirus-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transfection
- PMID: 24255584
- PMCID: PMC3828448
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.10.11
Apoptosis of bladder transitional cell carcinoma T24 cells induced by adenovirus-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transfection
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effects of adenovirus-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transfection on bladder transitional cell carcinoma T24 cells, and to provide novel insights and approaches to clinical therapies against bladder transitional cell carcinoma.
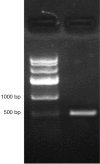
Methods: Firstly, construct recombinant adenovirus vector pAd-iNOS of iNOS, followed by transfection of pAd-iNOS into HECK293 packaging cells. Thirdly, harvest recombinant adenovirus rAd-iNOS after amplification and purification procedures. Finally, transfect the recombinant adenovirus rAd-iNOS into human bladder carcinoma T24 cells and examine the effect of rAd-iNOS transfection on apoptosis of T24 and possible mechanism.
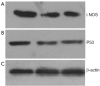
Results: As shown by this study, the recombinant adenovirus rAd-iNOS was constructed successfully. The virus titer was 5.8×10(8) PFU/mL and recombinant was verified by PCR analysis. Transfection of adenovirus rAd-iNOS into T24 cells could induce secretion of high NO concentration, P53 protein expression up-regulation, as well as promotion of T24 cell apoptosis.
Conclusions: The transfection of human bladder carcinoma T24 cells from recombinant adenovirus rAd-iNOS was confirmed to induce intracellular iNOS over-expression, high production of NO, up-regulation of intracellular P53 expression and promotion of cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; T24 cell line; gene therapy; iNOS gene.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[Effects of gene Livin transfection affect on the apoptosis in bladder carcinoma cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Mar 25;88(12):853-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18756993 Chinese.
-
Effect of silencing LRIG3 gene on the proliferation and apoptosis of bladder cancer T24 cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Apr;31(2):220. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0256-z. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21505989
-
Recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene transfer to genitourinary epithelium in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Gene Ther. 1995 Jun;2(2):97-104. Cancer Gene Ther. 1995. PMID: 7621262
-
The growth inhibitory effect of p21 adenovirus on human bladder cancer cells.J Urol. 2000 Mar;163(3):1033-8. J Urol. 2000. PMID: 10688044
-
Expression of a recombinant vector of a mutant human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene in human bladder cancer cell line T24, and its clinical significance.BJU Int. 2005 Oct;96(6):890-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05732.x. BJU Int. 2005. PMID: 16153224
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide-Mediated Enhancement and Reversal of Resistance of Anticancer Therapies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Sep 17;8(9):407. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090407. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31533363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic RALA/iNOS Nanoparticles: A Potent Gene Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer Coupled as a Biomarker of Treatment.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Mar 17;6:249-258. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 28325291 Free PMC article.
-
The apoptotic inducible effects of salicylic acid on hepatoma cell line: relationship with nitric oxide signaling.J Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Sep;11(3):245-253. doi: 10.1007/s12079-017-0380-z. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28185215 Free PMC article.
-
Non-viral nitric oxide-based gene therapy improves perfusion and liposomal doxorubicin sonopermeation in neuroblastoma models.Theranostics. 2023 Jun 4;13(10):3402-3418. doi: 10.7150/thno.81700. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37351172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muntané J, De la Rosa AJ, Marín LM, et al. Nitric oxide and cell death in liver Cancer cells. Mitochondrion 2013;13:257-62 - PubMed
-
- Hussain SP, Trivers GE, Hofseth LJ, et al. Nitric oxide, a mediator of inflammation, suppresses tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2004;64:6849-53 - PubMed
-
- Swana HS, Smith SD, Perrotta PL, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 1999;161:630-4 - PubMed
-
- Hayashi H, Kuwahara M, Fujisaki N, et al. Immunohistochemical findings of nitric oxide synthase expression in urothelial transitional cell carcinoma including dysplasia. Oncol Rep 2001;8:1275-9 - PubMed
-
- Kagoura M, Matsui C, Toyoda M, et al. Immunohistochemical study of inducible nitric oxide synthase in skin cancers. J Cutan Pathol 2001;28:476-81 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
