Aplastic anemia associated to systemic lupus erythematosus in an AIDS patient: a case report
- PMID: 24255622
- PMCID: PMC3832319
- DOI: 10.5581/1516-8484.20130100
Aplastic anemia associated to systemic lupus erythematosus in an AIDS patient: a case report
Abstract
Aplastic anemia is a bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by peripheral cytopenias and hypocellular bone marrow. Although aplastic anemia is idiopathic in most cases, rheumatic diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus are recognized as causes of aplastic anemia, with their possible etiological mechanisms being T and B lymphocyte dysfunction and pro-inflammatory cytokines and autoantibody production directed against bone marrow components. In the course of the human immunodeficiency virus infection/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, the identification of autoantibodies and the occurrence of rheumatic events, in addition to the natural course of systemic lupus erythematosus which is modified by immune changes that are characteristic of human immunodeficiency virus infection/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, make the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus challenging. This study reports the case of a woman with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome treated with a highly active antiretroviral therapy, who had prolonged cytopenias and hypocellular bone marrow consistent with aplastic anemia. The clinical picture, high autoantibodies titers, and sustained remission of the patient's hematological status through immunosuppression supported the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus-associated aplastic anemia. This is the first report of aplastic anemia concurrent with systemic lupus erythematosus and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, providing additional evidence that immune dysfunction is a key part of the pathophysiological mechanism of aplastic anemia.
Keywords: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; Anemia, aplastic; Autoantibodies; Case reports; Female; HIV infections; Humans; Lupus erythematosus, systemic; Pancytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interest
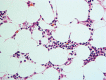
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aplastic anemia as a feature of systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report and literature review.Rheumatol Int. 2015 Jun;35(6):1073-82. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3162-4. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 25354463 Review.
-
Aplastic anemia in systemic lupus erythematosus: a distinct presentation of acquired aplastic anemia?J Clin Rheumatol. 2001 Dec;7(6):377-83. doi: 10.1097/00124743-200112000-00006. J Clin Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 17039179
-
Pancytopenia with aplastic anemia in systemic lupus erythematosus: case series and literature review.Rheumatol Int. 2024 May;44(5):943-953. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05585-6. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38512478 Review.
-
Special Education: Aplastic Anemia.Oncologist. 1996;1(3):187-189. Oncologist. 1996. PMID: 10387986
-
An antibody that inhibits in vitro bone marrow proliferation in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and aplastic anemia.Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):901-5. Arthritis Rheum. 1989. PMID: 2751721
Cited by
-
Microbe-Induced Inflammatory Signals Triggering Acquired Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 24;8:186. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00186. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28286502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Rare aplastic anemia in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a case series and systematic literature review.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 27;13:1602651. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1602651. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40656200 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant systemic lupus erythematosus and HIV infection: A rare case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(51):e9337. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009337. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29390513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hereditary Hemochromatosis Associated With Idiopathic Refractory Aplastic Anemia in a Five-Year-Old Boy: A Case Report.Cureus. 2021 Dec 3;13(12):e20135. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20135. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35003970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zandman-Goddard G, Shoenfeld Y. HIV and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2002;1(6):329–337. - PubMed
-
- Daikh BE, Holyst MM. Lupus-specific autoantibodies in concomitant human immunodeficiency virus and systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2001;30(6):418–425. - PubMed
-
- Alishiri GH, Saburi A, Bayat N, Saadat AR, Saburi E. The initial presentation of systemic lupus erythematosis with aplastic anemia successfully treated with rituximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(2):381–384. - PubMed
-
- Tabushi Y, Fukazawa T, Abe K, Kaneda K, Hirashima M, Young-Joon K, et al. A case of aplastic anemia in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod Rheumatol. 2003;13(2):177–180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
