Melatonin reduces bacterial translocation by preventing damage to the intestinal mucosa in an experimental severe acute pancreatitis rat model
- PMID: 24255660
- PMCID: PMC3829749
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.1338
Melatonin reduces bacterial translocation by preventing damage to the intestinal mucosa in an experimental severe acute pancreatitis rat model
Abstract
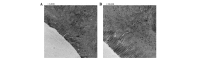
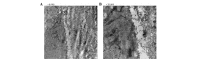
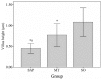
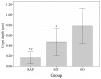
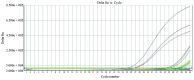
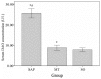
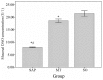
Recent studies have demonstrated that melatonin significantly decreased all studied acute pancreatitis-associated inflammatory parameters, in addition to reducing apoptosis and necrosis associated with pancreatic injury. However, the effect of melatonin on gut barrier dysfunction and bacterial translocation has not been fully elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of melatonin on intestinal integrity in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) to evaluate whether melatonin prevented intestine barrier dysfunction and reduced bacterial translocation. Forty male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into three groups, with 8 rats in the sham operation (SO) group, 18 rats in the SAP group and 14 SAP rats in the melatonin treatment (MT) group. SAP was induced by retrograde injection of 4% taurocholate into the biliopancreatic duct. Melatonin was administered 30 min prior to taurocholate injection in the melatonin-treated rats. All rats were sacrificed 24 h subsequent to pancreatitis induction. Real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to detect and quantify Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157 in postcava blood. The microvilli structure was also analyzed with transmission electron microscopy. The level of E. coli DNA in the MT group was significantly lower than in rats in the SAP group. No E. coli DNA was detected in the control group. Villus height and crypt depth in the ileum were significantly higher in the MT and control groups compared to the SAP group, and were significantly higher in the MT group than in the SAP group. These results suggested that melatonin prevented gut barrier dysfunction and reduced bacterial translocation, resulting in reduced pancreatic-associated infections and decreased early mortality rates.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; bacterial translocation; intestine barrier dysfunction; melatonin; microvilli structure.
Figures

References
-
- Petrov MS, Shanbhag S, Chakraborty M, Phillips AR, Windsor JA. Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:813–820. - PubMed
-
- Bettinger JR, Grendell JH. Intracellular events in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1991;6(Suppl 1):S2–S6. - PubMed
-
- Ammori BJ, Fitzgerald P, Hawkey P, McMahon MJ. The early increase in intestinal permeability and systemic endotoxin exposure in patients with severe acute pancreatitis is not associated with systemic bacterial translocation: molecular investigation of microbial DNA in the blood. Pancreas. 2003;26:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Gregoric P, Sijacki A, Stankovic S, et al. SIRS score on admission and initial concentration of IL-6 as severe acute pancreatitis outcome predictors. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Slavin J, Neoptolemos JP. Antibiotic prophylaxis in severe acute pancreatitis - what are the facts? Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2001;386:155–159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
