Lentinus edodes promotes fat removal in hypercholesterolemic mice
- PMID: 24255670
- PMCID: PMC3829752
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.1333
Lentinus edodes promotes fat removal in hypercholesterolemic mice
Abstract
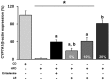
Lentinus (L.) edodes (shiitake mushroom) is used as a traditional medicine in Asia. One of the components of L. edodes, eritadenine (an adenosine analog alkaloid), has been shown to reduce cholesterol levels. The hypocholesterolemic action of eritadenine appears to be achieved through the modification of hepatic phospholipid metabolism. In the present study, the effects of L. edodes in a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia were investigated. Hypercholesterolemia was induced by the consumption of a high-fat diet (HFD). The animals were divided into six groups, which were fed a normal diet, HFD alone, HFD containing eritadenine [10 mg/kg of body weight (BW)] or HFD with 5, 10 or 20% L. edodes, respectively, for 4 weeks (from 5 to 9 weeks of age). The mice in the six groups had similar BW gains. Total serum cholesterol (T-CHO), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglyceride (TG) levels were increased in the HFD-fed group compared with those in the normal diet group. However, the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) were not significantly altered. In mice treated with L. edodes (5, 10 or 20%), the T-CHO, LDL and TG serum levels were reduced in a dose-dependent manner. The mRNA expression of cholesterol 7-α-hydroxylase 1 (CYP7A1) was decreased in hypercholesterolemic mice and increased by eritadenine and L. edodes (5, 10 and 20%) supplementation. In liver tissues, it was observed that lipid accumulation was reduced by treatment with eritadenine and L. edodes. In addition, it was revealed that the formation of atherosclerotic plaques due to the HFD was also suppressed by eritadenine and L. edodes. The results of the study indicated that the consumption of an HFD may inhibit CYP7A1 expression in the liver by increasing serum T-CHO, LDL and TG levels. L. edodes may help regulate lipid metabolism, suggesting that this fungus ameliorates hypercholesterolemia in mice by regulating CYP7A1 expression in the liver.
Keywords: CYP7A1; Lentinus edodes; eritadenine; hypercholesterolemia.
Figures

References
-
- Wasser SP. Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker; New York: 2005. Shiitake (Lentinus edodes) pp. 653–664. - DOI
-
- Ngai PH, Ng TB. Lentin, a novel and potent antifungal protein from shitake mushroom with inhibitory effects on activity of human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase and proliferation of leukemia cells. Life Sci. 2003;73:3363–3374. - PubMed
-
- Shimada Y, Morita T, Sugiyama K. Eritadenine-induced alterations of plasma lipoprotein lipid concentrations and phosphatidylcholine molecular species profile in rats fed cholesterol-free and cholesterol-enriched diets. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2003;67:996–1006. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama K, Akachi T, Yamakawa A. Hypocholesterolemic action of eritadenine is mediated by a modification of hepatic phospholipid metabolism in rats. J Nutr. 1995;125:2134–2144. - PubMed
-
- Shimada Y, Morita T, Sugiyama K. Dietary eritadenine and ethanolamine depress fatty acid desaturase activities by increasing liver microsomal phosphatidylethanolamine in rats. J Nutr. 2003;133:758–765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
